Machine Learning and Decision Support in Critical Care
- PMID: 27765959
- PMCID: PMC5066876
- DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2501978
Machine Learning and Decision Support in Critical Care
Abstract
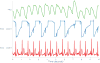
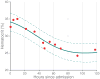
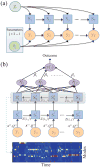
Clinical data management systems typically provide caregiver teams with useful information, derived from large, sometimes highly heterogeneous, data sources that are often changing dynamically. Over the last decade there has been a significant surge in interest in using these data sources, from simply re-using the standard clinical databases for event prediction or decision support, to including dynamic and patient-specific information into clinical monitoring and prediction problems. However, in most cases, commercial clinical databases have been designed to document clinical activity for reporting, liability and billing reasons, rather than for developing new algorithms. With increasing excitement surrounding "secondary use of medical records" and "Big Data" analytics, it is important to understand the limitations of current databases and what needs to change in order to enter an era of "precision medicine." This review article covers many of the issues involved in the collection and preprocessing of critical care data. The three challenges in critical care are considered: compartmentalization, corruption, and complexity. A range of applications addressing these issues are covered, including the modernization of static acuity scoring; on-line patient tracking; personalized prediction and risk assessment; artifact detection; state estimation; and incorporation of multimodal data sources such as genomic and free text data.
Keywords: Critical care; feature extraction; machine learning; signal processing.
Figures


References
-
- Pronovost P, Angus D, Dorman TR, Dremsizov KA, Young TT. Physician Staffing Patterns and Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patient: a Systematic Review. JAMA. 2002;288(17):2151–2162. - PubMed
-
- Kane R, Shamliyan T, Mueller C, Duval S, Wilt TJ. The association of registered nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medical Care. 2007 Dec;45(12):1195–1204. - PubMed
-
- Halpern NA, Pastores SM. Critical care medicine in the United States 2000–2005: An analysis of bed numbers, occupancy rates, payer mix, and costs*. Critical care medicine. 2010;38(1):65–71. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
