Deficiency of DJ-1 Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis through Inhibition of Hepatic ROS Production and Inflammation
- PMID: 27766037
- PMCID: PMC5069444
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.15154
Deficiency of DJ-1 Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis through Inhibition of Hepatic ROS Production and Inflammation
Abstract
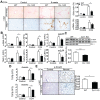
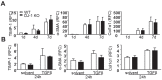
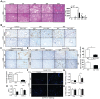
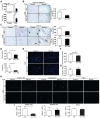
Liver fibrosis is a global health problem and previous studies have demonstrated that reactive oxygen species (ROS) play important roles in fibrogenesis. Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, early onset) 7 (Park7) also called DJ-1 has an essential role in modulating cellular ROS levels. DJ-1 therefore may play functions in liver fibrogenesis and modulation of DJ-1 may be a promising therapeutic approach. Here, wild-type (WT) and DJ-1 knockout (DJ-1 KO) mice were administrated with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) to induce liver fibrosis or acute liver injury. Results showed that DJ-1 depletion significantly blunted liver fibrosis, accompanied by marked reductions in liver injury and ROS production. In the acute CCl4 model, deficiency of DJ-1 showed hepatic protective functions as evidenced by decreased hepatic damage, reduced ROS levels, diminished hepatic inflammation and hepatocyte proliferation compared to WT mice. In vitro hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation assays indicated that DJ-1 has no direct effect on the activation of HSCs in the context of with or without TGFβ treatment. Thus our present study demonstrates that in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, DJ-1 deficiency attenuates mice fibrosis by inhibiting ROS production and liver injury, and further indirectly affecting the activation of HSCs. These results are in line with previous studies that ROS promote HSC activation and fibrosis development, and suggest the therapeutic value of DJ-1 in treatment of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: DJ-1; ROS; inflammation; lipid peroxidation.; liver fibrosis; liver injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DJ-1 deficiency attenuates expansion of liver progenitor cells through modulating the inflammatory and fibrogenic niches.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 9;7(6):e2257. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.161. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27277679 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid DJ-1 deficiency protects acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury through decreasing inflammatory response.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 21;13(14):18879-18893. doi: 10.18632/aging.203340. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34289451 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of NOX1 or NOX4 Prevents Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice through Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0129743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129743. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222337 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) and liver fibrosis: A review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2018 Aug;36(6):292-302. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3351. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2018. PMID: 30028028 Review.
-
Research progress of natural compounds in anti-liver fibrosis by affecting autophagy of hepatic stellate cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Feb;48(2):1915-1924. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06171-w. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33609264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS: Executioner of regulating cell death in spinal cord injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 23;15:1330678. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1330678. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From liver fibrosis to hepatocarcinogenesis: Role of excessive liver H2O2 and targeting nanotherapeutics.Bioact Mater. 2022 Nov 12;23:187-205. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.11.001. eCollection 2023 May. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 36406254 Free PMC article.
-
Park 7: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Macrophages in Sepsis-Induced Immunosuppression.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02632. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30542343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutual interaction between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Apr 13;19(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01210-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32284046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angelica Polysaccharide Antagonizes 5-FU-Induced Oxidative Stress Injury to Reduce Apoptosis in the Liver Through Nrf2 Pathway.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 16;11:720620. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.720620. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34485154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annual review of pathology. 2011;6:425–56. - PubMed
-
- Marra F. Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Frontiers in bioscience: a journal and virtual library. 2002;7:d1899–914. - PubMed
-
- Nieto N, Friedman SL, Cederbaum AI. Cytochrome P450 2E1-derived reactive oxygen species mediate paracrine stimulation of collagen I protein synthesis by hepatic stellate cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2002;277:9853–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

