New horizon in platelet function: with special reference to a recently-found molecule, CLEC-2
- PMID: 27766053
- PMCID: PMC5056494
- DOI: 10.1186/s12959-016-0099-8
New horizon in platelet function: with special reference to a recently-found molecule, CLEC-2
Abstract
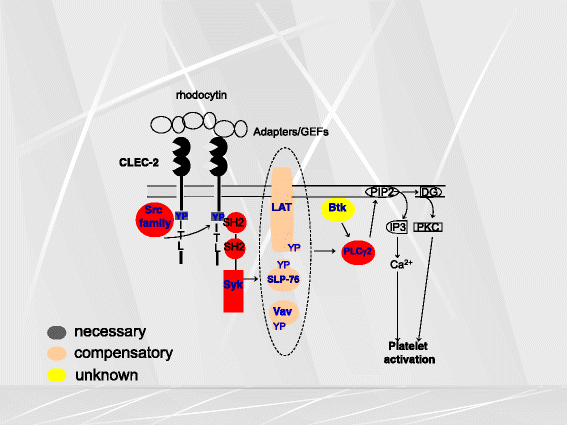
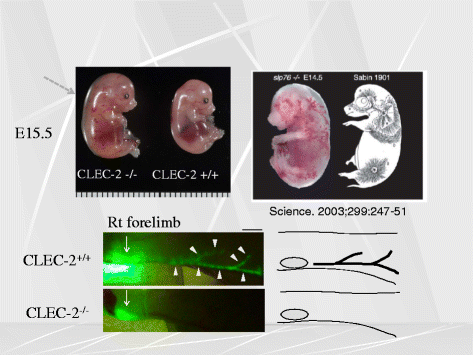
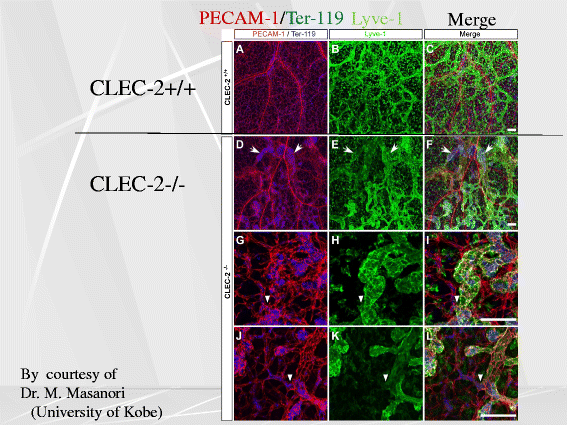
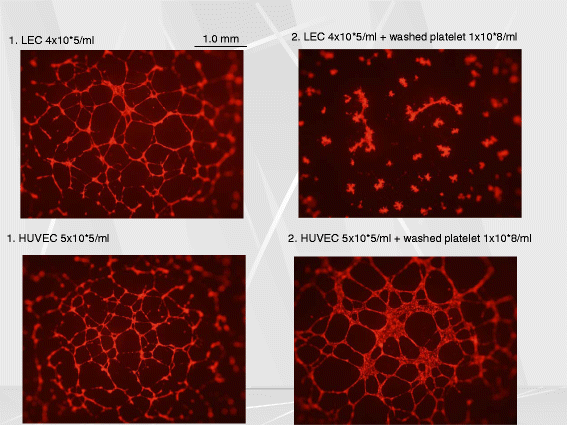
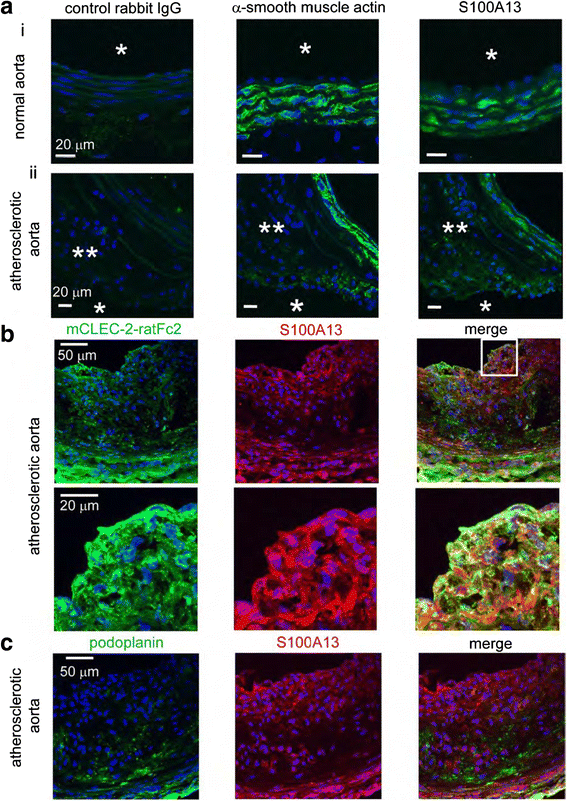
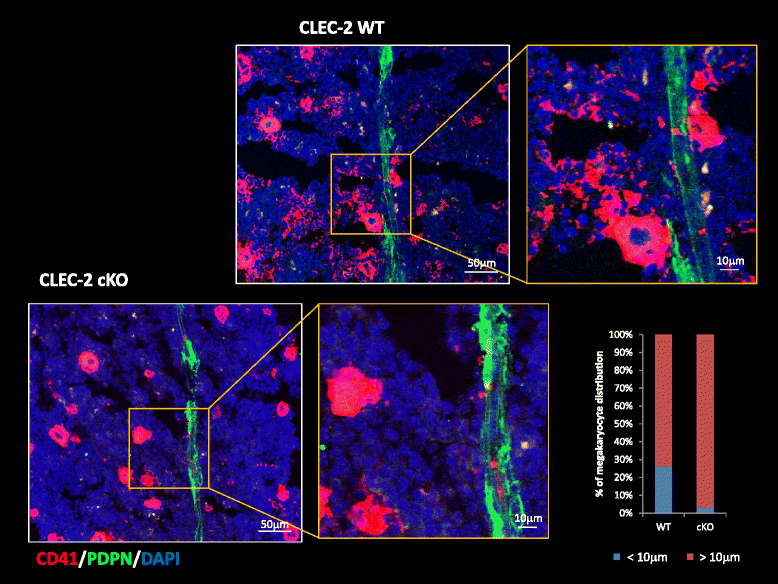
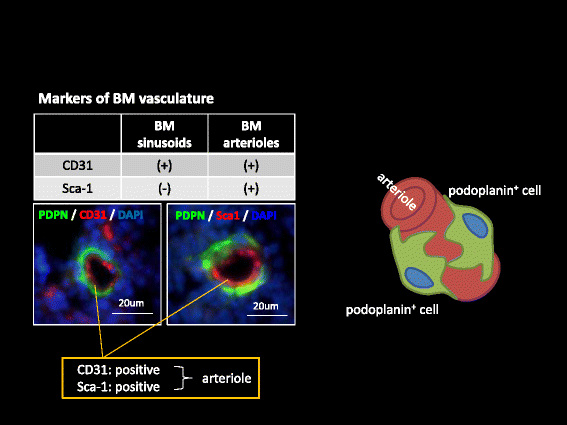
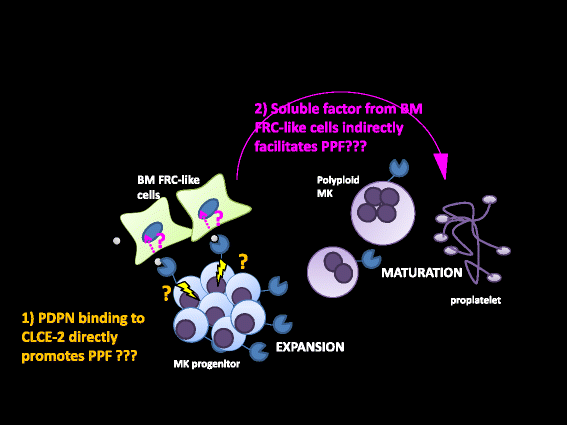
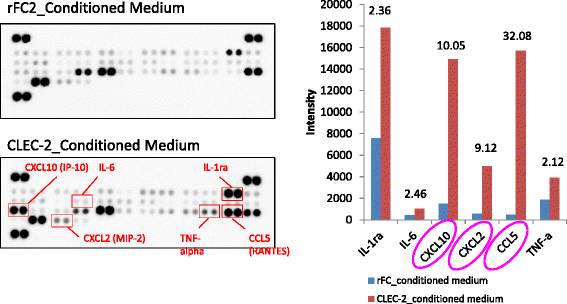
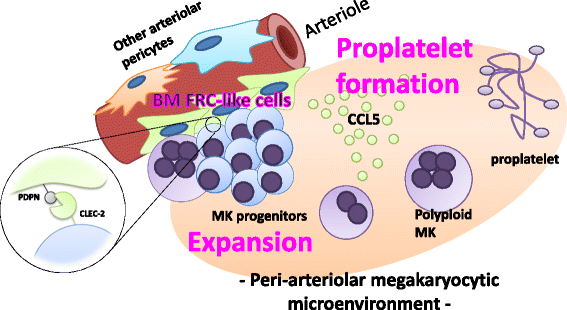
Platelets play a key role in the pathophysiological processes of hemostasis and thrombus formation. However, platelet functions beyond thrombosis and hemostasis have been increasingly identified in recent years. A large body of evidence now exists which suggests that platelets also play a key role in inflammation, immunity, malignancy, and furthermore in organ development and regeneration, such as the liver. We have recently identified CLEC-2 on the platelet membrane, which induces intracellular activation signals upon interaction of a snake venom, rhodocytin. Later we discovered that podoplanin, present in renal podocytes and lymphatic endothelial cells, both of which are not accessible to platelets in blood stream, is an endogenous ligand for CLEC-2. In accord with our expectation, platelet-specific CLEC-2 knockout mice have a phenotype of edema, lymphatic vessel dilatation, and the presence of blood cells in lymphatic vessels. It is suggested that lymphatic/blood vessel separation during the developmental stage is governed by cytokines released from platelets activated by the interaction between platelet CLEC-2 and podoplanin present on lymphatic endothelial cells. Recombinant CLEC-2 bound to early atherosclerotic lesions and normal arterial walls, co-localizing with vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry showed that recombinant CLEC-2, but not an anti-podoplanin antibody, bound to VSMCs, suggesting that CLEC-2 ligands other than podoplanin are present in VSMCs. Protein arrays and Biacore analysis were used to identify S100A13 as a CLEC-2 ligand in VSMCs. S100A13 was released upon oxidative stress, and expressed in the luminal area of atherosclerotic lesions. Megakaryopoiesis is promoted through the CLEC-2/podoplanin interaction in the vicinity of arterioles, not sinusoids or lymphatic vessels. There exist podoplanin-expressing bone-marrow (BM) arteriolar stromal cells, tentatively termed as BM fibroblastic reticular cell (FRC)-like cells, and megakaryocyte colonies were co-localized with periarteriolar BM FRC-like cells in the BM. CLEC-2/podoplanin interaction induces BM FRC-like cells to secrete CCL5 to facilitate proplatelet formation. These observations indicate that a reciprocal interaction with between CLEC-2 on megakaryocytes and podoplanin on BM FRC-like cells contributes to the periarteriolar megakaryopoietic microenvironment in mouse BM.
Keywords: Beyond hemostasis; CLEC-2; Immunity; Lymphangiogeneis; Megakaryopoiesis; Platelets; Smooth muscle cells; Thrombosis.
Figures
References
-
- Suzuki-Inoue K, Inoue O, Ding G, Nishimura S, Hokamura K, Eto K, et al. Essential in vivo roles of the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2: embryonic/neonatal lethalilty of CLEC-2-deficient mice by blood/lymphatic misconnections and impaired thrombus formation of CLEC-2-deficient platelets. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:24494–507. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130575. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

