Long Non-coding RNA TUSC7, a Target of miR-23b, Plays Tumor-Suppressing Roles in Human Gliomas
- PMID: 27766072
- PMCID: PMC5052253
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00235
Long Non-coding RNA TUSC7, a Target of miR-23b, Plays Tumor-Suppressing Roles in Human Gliomas
Abstract
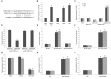
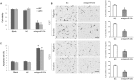
Tumour suppressor candidate 7 (TUSC7) is a novel tumor suppressor gene generating long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs) in several types of human cancers. The expression and function of TUSC7 in human brain glioma has yet to be elucidated. In this study, TUSC7 was poorly expressed in tissues and cell lines of glioma, and the lower expression was correlated with glioma of the worse histological grade. Moreover, TUSC7 is a prognostic biomarker of glioma patients. Up-regulation of TUSC7 suppressed cellular proliferation and invasion of glioma cells, and accelerated cellular apoptosis. Bioinformatics analysis showed that TUSC7 specifically binds to miR-23b. MiR-23b was up-regulated in glioma and negatively correlated with the expression of TUSC7. The miR-23b expression was inhibited remarkably by the upregulation of TUSC7 and the reciprocal inhibition was determined between TUSC7 and miR-23b.RNA pull-down and luciferase reporter assays were used to validate the sequence-specific correlation between miR-23b and TUSC7. TUSC7 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells and promoted cellular apoptosis largely bypassing miR-23b. We conclude that the lncRNA TUSC7 acted as a tumor suppressor gene negatively regulated by miR-23b, suggesting a novel therapeutic strategy against gliomas.
Keywords: TUSC7; glioma; mir-23b; noncoding RNA; tumor suppress gene.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

