Temporal Code-Driven Stimulation: Definition and Application to Electric Fish Signaling
- PMID: 27766078
- PMCID: PMC5052257
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2016.00041
Temporal Code-Driven Stimulation: Definition and Application to Electric Fish Signaling
Abstract
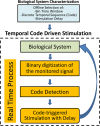
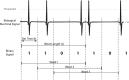
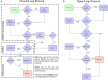
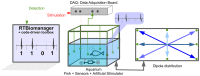
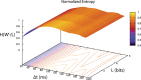
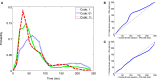
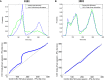
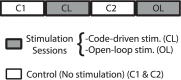
Closed-loop activity-dependent stimulation is a powerful methodology to assess information processing in biological systems. In this context, the development of novel protocols, their implementation in bioinformatics toolboxes and their application to different description levels open up a wide range of possibilities in the study of biological systems. We developed a methodology for studying biological signals representing them as temporal sequences of binary events. A specific sequence of these events (code) is chosen to deliver a predefined stimulation in a closed-loop manner. The response to this code-driven stimulation can be used to characterize the system. This methodology was implemented in a real time toolbox and tested in the context of electric fish signaling. We show that while there are codes that evoke a response that cannot be distinguished from a control recording without stimulation, other codes evoke a characteristic distinct response. We also compare the code-driven response to open-loop stimulation. The discussed experiments validate the proposed methodology and the software toolbox.
Keywords: computational biology; electric fish; information theory; neuroinformatics; signal processing.
Figures
References
-
- Bell C. C., Myers J. P., Russell C. J. (1974). Electric organ discharge patterns during dominance related behavioral displays ingnathonemus petersii (mormyridae). 92, 201–228. 10.1007/bf00694506 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

