Non-immunosuppressive triazole-based small molecule induces anticancer activity against human hormone-refractory prostate cancers: the role in inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and c-Myc signaling pathways
- PMID: 27769069
- PMCID: PMC5363565
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12765
Non-immunosuppressive triazole-based small molecule induces anticancer activity against human hormone-refractory prostate cancers: the role in inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and c-Myc signaling pathways
Abstract
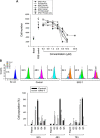
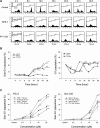
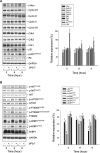
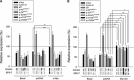
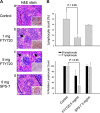
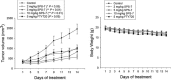
A series of triazole-based small molecules that mimic FTY720-mediated anticancer activity but minimize its immunosuppressive effect have been produced. SPS-7 is the most effective derivative displaying higher activity than FTY720 in anti-proliferation against human hormone-refractory prostate cancer (HRPC). It induced G1 arrest of cell cycle and subsequent apoptosis in thymidine block-mediated synchronization model. The data were supported by a decrease of cyclin D1 expression, a dramatic increase of p21 expression and an associated decrease in RB phosphorylation. c-Myc overexpression replenished protein levels of cyclin D1 indicating that c-Myc was responsible for cell cycle regulation. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways through p70S6K- and 4EBP1-mediated translational regulation are critical to cell proliferation and survival. SPS-7 significantly inhibited this translational pathway. Overexpression of Myr-Akt (constitutively active Akt) completely abolished SPS-7-induced inhibitory effect on mTOR/p70S6K/4EBP1 signaling and c-Myc protein expression, suggesting that PI3K/Akt serves as a key upstream regulator. SPS-7 also demonstrated substantial anti-tumor efficacy in an in vivo xenograft study using PC-3 mouse model. Notably, FTY720 but not SPS-7 induced a significant immunosuppressive effect as evidenced by depletion of marginal zone B cells, down-regulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors and a decrease in peripheral blood lymphocytes. In conclusion, the data suggest that SPS-7 is not an immunosuppressant while induces anticancer effect against HRPC through inhibition of Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathwaysthat down-regulate protein levels of both c-Myc and cyclin D1, leading to G1 arrest of cell cycle and subsequent apoptosis. The data also indicate the potential of SPS-7 since PI3K/Akt signalingis responsive for the genomic alterations in prostate cancer.
Keywords: Myc; PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling; autophagy; non-immunosuppression; triazole-base.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The (+)-Brevipolide H Displays Anticancer Activity against Human Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: The Role of Oxidative Stress and Akt/mTOR/p70S6K-Dependent Pathways in G1 Checkpoint Arrest and Apoptosis.Molecules. 2020 Jun 25;25(12):2929. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122929. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32630532 Free PMC article.
-
Concomitant reduction of c-Myc expression and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling by quercetin induces a strong cytotoxic effect against Burkitt's lymphoma.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Oct;79:393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27620077
-
Luteoloside induces G0/G1 arrest and pro-death autophagy through the ROS-mediated AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signalling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Dec 9;494(1-2):263-269. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.042. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 29024631
-
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013 May 20;20(3):R83-99. doi: 10.1530/ERC-12-0394. Print 2013 Jun. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23456430 Review.
-
PI3K/ Akt/ mTOR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(12):1217-1226. doi: 10.2174/1389450120666190618123846. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 31215384 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting MYC Dependence by Metabolic Inhibitors in Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2017 Mar 31;8(4):114. doi: 10.3390/genes8040114. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28362357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Reductase 1: a novel target for sensitizing multiple myeloma cells to bortezomib by inhibition of PRAS40-mediated protein synthesis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 1;41(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02250-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35105345 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Prostate Cancer Chemoprevention and Intervention.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 3;13(8):1195. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081195. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin and FTY720 Alleviate Atherosclerosis by Cross Talk of Macrophage Polarization and Autophagy.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Dec 6;2018:1010248. doi: 10.1155/2018/1010248. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30627532 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Metabolism as a Therapeutic Avenue for Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 12;15(10):2732. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102732. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elfiky AA, Jiang Z. The PI3 kinase signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013;13:157–164. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

