Computational pan-genomics: status, promises and challenges
- PMID: 27769991
- PMCID: PMC5862344
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbw089
Computational pan-genomics: status, promises and challenges
Abstract
Many disciplines, from human genetics and oncology to plant breeding, microbiology and virology, commonly face the challenge of analyzing rapidly increasing numbers of genomes. In case of Homo sapiens, the number of sequenced genomes will approach hundreds of thousands in the next few years. Simply scaling up established bioinformatics pipelines will not be sufficient for leveraging the full potential of such rich genomic data sets. Instead, novel, qualitatively different computational methods and paradigms are needed. We will witness the rapid extension of computational pan-genomics, a new sub-area of research in computational biology. In this article, we generalize existing definitions and understand a pan-genome as any collection of genomic sequences to be analyzed jointly or to be used as a reference. We examine already available approaches to construct and use pan-genomes, discuss the potential benefits of future technologies and methodologies and review open challenges from the vantage point of the above-mentioned biological disciplines. As a prominent example for a computational paradigm shift, we particularly highlight the transition from the representation of reference genomes as strings to representations as graphs. We outline how this and other challenges from different application domains translate into common computational problems, point out relevant bioinformatics techniques and identify open problems in computer science. With this review, we aim to increase awareness that a joint approach to computational pan-genomics can help address many of the problems currently faced in various domains.
Keywords: data structures; haplotypes; pan-genome; read mapping; sequence graph.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

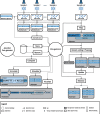
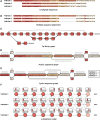
References
-
- Fleischmann RD, Adams MD, White O, et al. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 1995;269(5223):496–512. - PubMed
-
- Goffeau A, Barrell BG, Bussey H, et al. Life with 6000 genes. Science 1996;274(5287):546–67. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001;409(6822):860–921. - PubMed
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 2001;291(5507):1304–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

