Objective, computerized video-based rating of blepharospasm severity
- PMID: 27770067
- PMCID: PMC5109937
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003336
Objective, computerized video-based rating of blepharospasm severity
Abstract
Objective: To compare clinical rating scales of blepharospasm severity with involuntary eye closures measured automatically from patient videos with contemporary facial expression software.
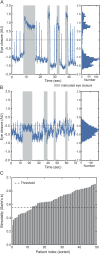
Methods: We evaluated video recordings of a standardized clinical examination from 50 patients with blepharospasm in the Dystonia Coalition's Natural History and Biorepository study. Eye closures were measured on a frame-by-frame basis with software known as the Computer Expression Recognition Toolbox (CERT). The proportion of eye closure time was compared with 3 commonly used clinical rating scales: the Burke-Fahn-Marsden Dystonia Rating Scale, Global Dystonia Rating Scale, and Jankovic Rating Scale.
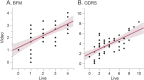
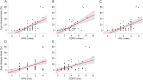
Results: CERT was reliably able to find the face, and its eye closure measure was correlated with all of the clinical severity ratings (Spearman ρ = 0.56, 0.52, and 0.56 for the Burke-Fahn-Marsden Dystonia Rating Scale, Global Dystonia Rating Scale, and Jankovic Rating Scale, respectively, all p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that CERT has convergent validity with conventional clinical rating scales and can be used with video recordings to measure blepharospasm symptom severity automatically and objectively. Unlike EMG and kinematics, CERT requires only conventional video recordings and can therefore be more easily adopted for use in the clinic.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Price KM, Ramey NA, Richard MJ, Woodward DJ, Woodward JA. Can methylphenidate objectively provide relief in patients with uncontrolled blepharospasm? A pilot study using surface electromyography. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2010;26:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Fahn S, Marsden CD, Bressman SB, Moskowitz C, Friedman J. Validity and reliability of a rating-scale for the primary torsion dystonias. Neurology 1985;35:73–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 EB009282/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079076/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050263/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD033113/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS077946/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086883/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075321/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020002/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041509/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 TR001456/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094670/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES021488/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030749/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS075527/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS090214/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059740/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058714/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS077959/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 NS077384/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
