Longitudinal and Horizontal Load Testing of Inflatable Penile Implant Cylinders of Two Manufacturers: An Ex Vivo Demonstration of Inflated Rigidity
- PMID: 27770856
- PMCID: PMC5654325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.09.015
Longitudinal and Horizontal Load Testing of Inflatable Penile Implant Cylinders of Two Manufacturers: An Ex Vivo Demonstration of Inflated Rigidity
Abstract
Introduction: Since the inception of the inflatable penile prosthesis, a new era has been ushered in for the management of erectile dysfunction. Despite multiple innovations to improve function and reliability, there are no current data comparing the biomechanical properties of these devices.
Aim: To compare the resistance of the Coloplast Titan (Minneapolis, MN, USA) with that of the AMS 700 LGX (Minnetonka, MN, USA) penile prosthesis cylinders to longitudinal (penetration) and horizontal (gravity) forces.
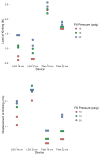
Methods: We compared two cylinder sizes from each company: the Coloplast Titan (18 and 22 cm) and the AMS 700 LGX (18 and 21 cm). To evaluate axial rigidity, which simulates forces during penetration, we performed a longitudinal load compression test to determine the load required to cause the cylinder to kink. To test horizontal rigidity, which simulates the horizontal forces exerted by gravity, we performed a modified cantilever test and measured the degrees of bend for each device. All devices were tested at 10, 15, and 20 PSI to simulate in vivo pressures.
Main outcome measures: The main outcome measurement for the longitudinal load test (penetration) was the force required for the inflated cylinder to bend, thereby affecting its rigidity. The main outcome for the horizontal rigidity test (gravity) was the angle of displacement, in which a smaller angle represents a more horizontally rigid device.
Results: Longitudinal column testing (penetration) demonstrated that less force was required for the AMS device to kink compared with the Coloplast implant across all three fill pressures tested. The Coloplast Titan also had a smaller angle of displacement at the modified cantilever test (gravity) compared with the AMS implant across all fill pressures.
Conclusion: The Coloplast Titan demonstrated greater resistance to longitudinal (penetration) and horizontal (gravity) forces in this study. The AMS device was very sensitive to fill pressures. In contrast, the Coloplast Titan's ability to resist these forces was less dependent on the device fill pressure.
Keywords: Erectile Dysfunction; Material Properties; Prosthesis.
Copyright © 2016 International Society for Sexual Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Chung E, Solomon M, DeYoung L, Brock GB. Comparison between AMS 700 CX and Coloplast Titan inflatable penile prosthesis for Peyronie’s disease treatment and remodeling: clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. The journal of sexual medicine. 2013;10:2855–60. - PubMed
-
- Hakky TS, Wang R, Henry GD. The evolution of the inflatable penile prosthetic device and surgical innovations with anatomical considerations. Current urology reports. 2014;15:410. - PubMed
-
- Henry GD. Historical review of penile prosthesis design and surgical techniques: part 1 of a three-part review series on penile prosthetic surgery. The journal of sexual medicine. 2009;6:675–81. - PubMed
-
- Mulcahy JJ. The Development of Modern Penile Implants. Sexual medicine reviews. 2016;4:177–89. - PubMed
-
- Wilson SK, Henry GD, Delk JR, Jr, Cleves MA. The mentor Alpha 1 penile prosthesis with reservoir lock-out valve: effective prevention of auto-inflation with improved capability for ectopic reservoir placement. The Journal of urology. 2002;168:1475–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

