Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Management of Chronic Watery Diarrhea
- PMID: 27773805
- PMCID: PMC5285476
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.014
Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Management of Chronic Watery Diarrhea
Abstract
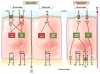
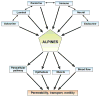
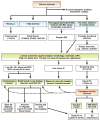
Chronic watery diarrhea poses a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge and is often a disabling condition for patients. Although acute diarrhea is likely to be caused by infection, the causes of chronic diarrhea (>4 weeks in duration) are more elusive. We review the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic diarrhea. Drawing on recent insights into the molecular mechanisms of intestinal epithelial transport and barrier function, we discuss how diarrhea can result from a decrease in luminal solute absorption, an increase in secretion, or both, as well as derangements in barrier properties. We also describe the various extraepithelial factors that activate diarrheal mechanisms. Finally, clinical evaluation and tests used in the assessment of patients presenting with chronic diarrhea are reviewed, and an algorithm guiding therapeutic decisions and pharmacotherapy is presented.
Keywords: Diarrhea; Management; Pathophysiology.
Copyright © 2017 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schiller LR, Pardi DS, Spiller R, Spiller R, Semrad CE, Surawicz CM, Giannella RA, Krejs GJ, Farthing MJ, Sellin JH. Gastro 2013 APDW/WCOG Shanghai working party report: chronic diarrhea: definition, classification, diagnosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:6–25. - PubMed
-
- Barrett KE, Keely SJ. Integrative physiology and pathophysiology of intestinal electrolyte transport. In: Johnson LR, Barrett KE, Gishan FK, Merchant JL, Said HM, Wood JD, editors. Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract. 4. Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2006. pp. 1931–1951.
-
- Zachos NC, Tse M, Donowitz M. Molecular physiology of intestinal Na+/H+ exchange. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:411–443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

