Intradermal grass pollen immunotherapy increases TH2 and IgE responses and worsens respiratory allergic symptoms
- PMID: 27773851
- PMCID: PMC5457129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.024
Intradermal grass pollen immunotherapy increases TH2 and IgE responses and worsens respiratory allergic symptoms
Abstract
Background: Repeated low-dose grass pollen intradermal allergen injection suppresses allergen-induced cutaneous late-phase responses comparably with conventional subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy.
Objective: We sought to evaluate the efficacy and safety of grass pollen intradermal immunotherapy in the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
Methods: We randomly assigned 93 adults with grass pollen-induced allergic rhinitis to receive 7 preseasonal intradermal allergen injections (containing 7 ng of Phl p 5 major allergen) or a histamine control. The primary end point was daily combined symptom-medication scores during the 2013 pollen season (area under the curve). Analysis was by intention to treat. Skin biopsy specimens were collected after intradermal allergen challenges, and late-phase responses were measured 4 and 7, 10, or 13 months after treatment.
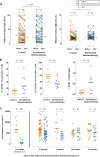
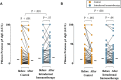
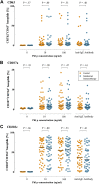
Results: There was no significant difference in the primary end point between treatment arms (active, n = 46; control, n = 47; median difference, 14; 95% CI, -172.5 to 215.1; P = .80). Among secondary end points, nasal symptoms were worse in the intradermal treatment group, as measured based on daily (median difference, 35; 95% CI, 4.0-67.5; P = .03) and visual analog scale (median difference, 53; 95% CI, -11.6 to 125.2; P = .05) scores. In a per-protocol analysis intradermal immunotherapy was further associated with worse asthma symptoms and fewer symptom-free days. Intradermal immunotherapy increased serum Phleum pratense-specific IgE levels (P = .001) compared with those in the control arm. T cells cultured from biopsy specimens of subjects undergoing intradermal immunotherapy had higher expression of the TH2 surface marker CRTH2 (P = .04) and lower expression of the TH1 marker CXCR3 (P = .01), respectively. Late-phase responses remained inhibited 7 months after treatment (P = .03).
Conclusion: Intradermal allergen immunotherapy suppressed skin late-phase responses but was not clinically effective and resulted in worsening of respiratory allergic symptoms.
Keywords: Allergy immunotherapy; Phleum pratense; allergic rhinitis; grass pollen; immunotherapy; intradermal; low dose.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Kiel M.A., Roder E., Gerth van Wijk R., Al M.J., Hop W.C., Rutten-van Molken M.P. Real-life compliance and persistence among users of subcutaneous and sublingual allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132:353–360.e2. - PubMed
-
- Kay A.B., Ying S., Varney V., Gaga M., Durham S.R., Moqbel R. Messenger RNA expression of the cytokine gene cluster, interleukin 3 (IL-3), IL-4, IL-5, and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, in allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. J Exp Med. 1991;173:775–778. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rotiroti G., Shamji M., Durham S.R., Till S.J. Repeated low-dose intradermal allergen injection suppresses allergen-induced cutaneous late responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:918–924.e1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

