Pragmatic research and outcomes in asthma and COPD
- PMID: 27774014
- PMCID: PMC5045006
- DOI: 10.2147/POR.S16671
Pragmatic research and outcomes in asthma and COPD
Abstract
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are common diseases which cause patients and society considerable difficulties. These are costly diseases which cause substantial morbidity and death. Health care policy makers have made improving outcomes in asthma and COPD a priority. Application of guideline recommended approaches to asthma and COPD care in the real-life setting has been emphasized but outcomes have not improved. Failure to improve outcomes may not be because of inconsistent applications of guideline recommendations, but rather because there are difficulties implementing the Expert Panel Report III (EPR 3) method for categorizing asthma severity and the Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) method for diagnosing COPD. As these serve as the foundation for treatment recommendations for these diseases, alternative approaches should be considered for categorizing asthma severity and identifying COPD patients. Claims-based algorithms provide an intriguing option for identifying persistent asthma patients and symptomatic COPD patients in administrative databases. These methods could be used as the basis for pragmatic research, both retrospective and prospective, on assessing outcomes of guideline recommended treatment approaches in asthma and COPD. Important questions urgently need to be answered about how guideline recommended approaches regarding use of long-acting inhaled β-agonist/inhaled corticosteroid (LABA/ICS) in asthma and long-acting inhaled anti-muscarinic agent (LAMA) and LABA/ICS in COPD affect outcomes in real-life situations.
Keywords: asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; pragmatic research.
Figures

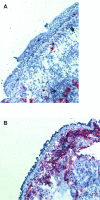
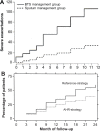
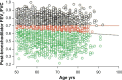
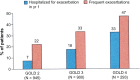
Similar articles
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Long-Acting Beta2 -Agonist Combined with a Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist or Inhaled Corticosteroid in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Apr;37(4):447-455. doi: 10.1002/phar.1913. Pharmacotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28226405
-
Role of Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist/Long-Acting β2-Agonist Therapy in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;51(8):696-705. doi: 10.1177/1060028017705149. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Ann Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28410560 Review.
-
Respiratory medication used in COPD patients from seven Latin American countries: the LASSYC study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018 May 11;13:1545-1556. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S154097. eCollection 2018. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018. PMID: 29785104 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty-five statements on early initiation of fixed combination ICS/LABA treatment for asthma and COPD in primary and secondary care: consensus research by a modified Delphi process.Pneumologie. 2012 Sep;66(9):549-57. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1310076. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Pneumologie. 2012. PMID: 22899206
-
Current evidence for COPD management with dual long-acting muscarinic antagonist/long-acting β2-agonist bronchodilators.Postgrad Med. 2020 Mar;132(2):198-205. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1702834. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 31900019 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhaled corticosteroid use in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the risk of pneumonia: a retrospective claims data analysis.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013;8:295-304. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S42366. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013. PMID: 23836970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Health Statistics Asthma. [Accessed October 5, 2011]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/Asthma/
-
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, Weinberger SE, et al. Diagnosis and management of stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a clinical practice guideline update from the American College of Physicians, American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, and European Respiratory Society. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(3):179–191. - PubMed
-
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute COPD for Health Care Professionals. [Accessed October 5, 2011]. Available from: http://www.nhlbi.gov/health/public/lung/copd/index.htm.
-
- Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan VH, Slejko JF, Belozeroff V, Globe DR, Lin SL. The burden of adult asthma in the United States: evidence from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(2):363–369. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – United States, 2000–2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2008;57(45):1229–1232. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

