SR-BI: Linking Cholesterol and Lipoprotein Metabolism with Breast and Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 27774064
- PMCID: PMC5054001
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00338
SR-BI: Linking Cholesterol and Lipoprotein Metabolism with Breast and Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Studies have demonstrated the significant role of cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism in the progression of cancer. The SCARB1 gene encodes the scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI), which is an 82-kDa glycoprotein with two transmembrane domains separated by a large extracellular loop. SR-BI plays an important role in the regulation of cholesterol exchange between cells and high-density lipoproteins. Accordingly, hepatic SR-BI has been shown to play an essential role in the regulation of the reverse cholesterol transport pathway, which promotes the removal and excretion of excess body cholesterol. In the context of atherosclerosis, SR-BI has been implicated in the regulation of intracellular signaling, lipid accumulation, foam cell formation, and cellular apoptosis. Furthermore, since lipid metabolism is a relevant target for cancer treatment, recent studies have focused on examining the role of SR-BI in this pathology. While signaling pathways have initially been explored in non-tumoral cells, studies with cancer cells have now demonstrated SR-BI's function in tumor progression. In this review, we will discuss the role of SR-BI during tumor development and malignant progression. In addition, we will provide insights into the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the SCARB1 gene. Overall, studying the role of SR-BI in tumor development and progression should allow us to gain useful information for the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: HDL cholesterol; SR-BI; breast cancer; cholesterol; lipoprotein.
Figures
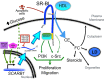
References
-
- Acton S. L., Scherer P. E., Lodish H. F., Krieger M. (1994). Expression cloning of SR-BI, a CD36-related class B scavenger receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 21003–21009. - PubMed
-
- Babitt J., Trigatti B., Rigotti A., Smart E. J., Anderson R. G., Xu S., et al. (1997). Murine SR-BI, a high density lipoprotein receptor that mediates selective lipid uptake, is N-glycosylated and fatty acylated and colocalizes with plasma membrane caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 13242–13249. 10.1074/jbc.272.20.13242 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

