Dose Assessment of Cefquinome by Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling in Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus Mastitis
- PMID: 27774090
- PMCID: PMC5053985
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01595
Dose Assessment of Cefquinome by Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling in Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus Mastitis
Abstract
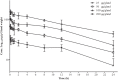
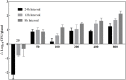
This work aimed to characterize the mammary gland pharmacokinetics of cefquinome after an intramammary administration and integrate pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. The pharmacokinetic profiles of cefquinome in gland tissue were measured using high performance liquid chromatograph. Therapeutic regimens covered various dosages ranging from 25 to 800 μg/gland and multiple dosing intervals of 8, 12, and 24 h. The in vivo bacterial killing activity elevated when dosage increased or when dosing intervals were shortened. The best antibacterial effect was demonstrated by a mean 1.5 log10CFU/gland visible count reduction. On the other hand, the results showed that the percentage of time duration of drug concentration exceeding the MIC during a dose interval (%T > MIC) was generally 100% because of the influence of drug distribution caused by the blood-milk barrier. Therefore, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameter of the ratio of area under the concentration-time curve over 24 h to the MIC (AUC0-24/MIC) was used to describe the efficacy of cefquinome instead of %T > MIC. When the magnitude of AUC0-24/MIC exceeding 16571.55 h⋅mL/g, considerable activity of about 1.5 log10CFU/g gland bacterial count reduction was observed in vivo. Based on the Monte Carlo simulation, the clinical recommended regimen of three infusions of 75 mg per quarter every 12 h can achieve a 76.67% cure rate in clinical treatment of bovine mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; PK/PD; cefquinome; dose assessment; mastitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ex Vivo Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Modeling and Optimal Regimens Evaluation of Cefquinome Against Bovine Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 8;9:837882. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.837882. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35350432 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics of Cefquinome in an Experimental Mouse Model of Staphylococcus Aureus Mastitis following Intramammary Infusion.PLoS One. 2016 May 24;11(5):e0156273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156273. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27218674 Free PMC article.
-
PK/PD Modeling to Assess Rifaximin Clinical Dosage in a Mouse Model of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Mastitis.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Jun 14;8:651369. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.651369. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34195244 Free PMC article.
-
PK/PD integration and pharmacodynamic cutoff of cefquinome against cow mastitis due to Escherichia coli.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;45(1):83-91. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13012. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34469000
-
How predictive is PK/PD for antibacterial agents?Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002 Apr;19(4):333-9. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(02)00029-8. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002. PMID: 11978504 Review.
Cited by
-
From Herd Health to Public Health: Digital Tools for Combating Antibiotic Resistance in Dairy Farms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 9;13(7):634. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070634. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to Cefquinome Sulfate in an In Vitro Pharmacokinetic Model with Transcriptomic Insights.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 2;13(2):329. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020329. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005696 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Cefquinome against Escherichia coli Environmental Mastitis Assessed by Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Integration in Lactating Mouse Model.Front Microbiol. 2017 Aug 2;8:1445. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01445. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28824576 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cefquinome against Streptococcus agalactiae in a murine mastitis model.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 25;18(1):e0278306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278306. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36696421 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Modeling and Optimal Regimens Evaluation of Cefquinome Against Bovine Mastitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 8;9:837882. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.837882. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35350432 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

