Antioxidant effects of Spirulina supplement against lead acetate-induced hepatic injury in rats
- PMID: 27774414
- PMCID: PMC5067858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2015.02.001
Antioxidant effects of Spirulina supplement against lead acetate-induced hepatic injury in rats
Abstract
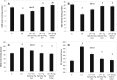
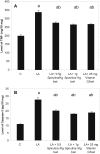
Lead is a toxic metal that induces a wide range of behavioral, biochemical and physiological effects in humans. Oxidative damage has been proposed as a possible mechanism involved in lead toxicity. The current study was carried out to evaluate the antioxidant activities of Spirulina supplement against lead acetate -induced hepatic injury in rats. Five groups of rats were used in this study, Control, Lead acetate (100 mg/kg), Lead acetate (100 mg/kg) + 0.5 g/kg Spirulina, Lead acetate (100 mg/kg) + 1 g/kg Spirulina and Lead acetate + 25 mg/100 g Vitamin C (reference drug). All experimental groups received the oral treatment by stomach tube once daily for 4 weeks. Lead intoxication resulted in a significant increase in serum alanine transaminae (ALT), aspartate transaminae (AST) activities, liver homogenate tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), caspase-3, malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) levels and a significant decline of total serum protein, liver homogenate reduced glutathione (GSH) level and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Both doses of Spirulina supplement as well as Vitamin C succeeded to improve the biochemical parameters of serum and liver and prevented the lead acetate-induced significant changes on plasma and antioxidant status of the liver. Both doses of Spirulina supplement had the same anti-apoptotic activity and high dose exhibited more antioxidant activity than that of low dose. In conclusion, the results of the present work revealed that Spirulina supplement had protective, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects on lead acetate-induced hepatic damage.
Keywords: Caspase-3; Spirulina supplement; Tumor necrosis factor-α; anti-apoptotic; lead acetate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of Spirulina maxima on hyperlipidemia and oxidative-stress induced by lead acetate in the liver and kidney.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Mar 31;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-35. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20353607 Free PMC article.
-
Spirulina exhibits hepatoprotective effects against lead induced oxidative injury in newborn rats.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Aug 31;62(10):85-3. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016. PMID: 27609480
-
The Potency of Red Seaweed (Eucheuma cottonii) Extracts as Hepatoprotector on Lead Acetate-induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jul-Sep;9(3):282-286. doi: 10.4103/pr.pr_69_16. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28827971 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorella vulgaris or Spirulina platensis mitigate lead acetate-induced testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis with regard to androgen receptor expression in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Aug;28(29):39126-39138. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13411-w. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33754266
-
Antagonistic Efficacy of Luteolin against Lead Acetate Exposure-Associated with Hepatotoxicity is Mediated via Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 21;9(1):10. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010010. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877779 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protective Effect of Spirulina platensis Extract against Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 29;11(10):2309. doi: 10.3390/nu11102309. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31569451 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Attenuates Lead-Induced Cerebellar Toxicity in Rats via Chelating Activity and Inhibition of Oxidative Stress.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 6;9(9):453. doi: 10.3390/biom9090453. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31489882 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Opuntia dillenii Haw Fruit against Lead Acetate-Induced Hepatotoxicity: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 29;2021:6698345. doi: 10.1155/2021/6698345. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34012476 Free PMC article.
-
Arctium lappa Root Extract Prevents Lead-Induced Liver Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, and Activating Akt/GSK-3β Signaling.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Nov 24;8(12):582. doi: 10.3390/antiox8120582. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31771282 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective and Neuroprotective Effects of Naringenin against Lead-Induced Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 3;11(4):1080. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041080. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Godwin H.A. The biological chemistry of lead. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001;5:223–227. - PubMed
-
- WHO Lead poisoning and health, Fact sheet N°379 Reviewed October 2014.
-
- Rahman S., Sultana S. Chemopreventive activity of glycyrrhizin on lead acetate mediated hepatic oxidative stress and its hyperproliferative activity inWistar rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2006;160:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Bolin C.M., Basha R., Cox D. Exposure to lead and the developmental origin of oxidative DNA damage in the aging brain. FASEB J. 2006;20:788–790. - PubMed
-
- Hsu C.P., Guo L.Y. Antioxidant nutrients and lead toxicity. Toxicol. 2002;180:33–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
