Psoriasis-Specific RNA Isoforms Identified by RNA-Seq Analysis of 173,446 Transcripts
- PMID: 27774448
- PMCID: PMC5053979
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2016.00046
Psoriasis-Specific RNA Isoforms Identified by RNA-Seq Analysis of 173,446 Transcripts
Abstract
Background: Several studies have been published that investigated potential links between transcriptome changes and psoriasis using microarrays and RNA-seq technologies, but no previous study has analyzed expression profile of alternatively spliced transcripts in psoriasis.
Objectives: Identification of potential alternatively spliced RNA isoforms with disease-specific expression profile.
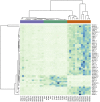
Methods: Using our published RNA sequencing data from lesional psoriatic (LP), non-lesional psoriatic (NLP), and normal control skin (C), we analyzed the differential expression of RNA splicing variants. LP sample was compared with NLP, as was LP with C and NLP with C.
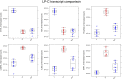
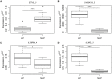
Results: Transcript-based annotation analyzed 173,446 transcripts (RNA isoforms), and around 9,000 transcripts were identified as differentially expressed between study groups. Several previously undescribed RNA variants were found. For instance, transcript ETV3_3 (ENST00000326786) was significantly downregulated in LP and NLP skin. ETV3 is a transcriptional repressor that contributes to the downstream anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10. We also identified diseases-specific transcripts (S100A7A, IL36RN_4, and IL36G_3) of genes already recognized to be involved in inflammation and immune response.
Conclusion: Psoriasis is characterized by significant differences in the expression of RNA alternative isoforms. Description of these new isoforms improves our knowledge about this complex disease.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; psoriasis; transcript expression profiling; transcriptome.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

