Social transfer of pain in mice
- PMID: 27774512
- PMCID: PMC5072181
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1600855
Social transfer of pain in mice
Abstract
A complex relationship exists between the psychosocial environment and the perception and experience of pain, and the mechanisms of the social communication of pain have yet to be elucidated. The present study examined the social communication of pain and demonstrates that "bystander" mice housed and tested in the same room as mice subjected to inflammatory pain or withdrawal from morphine or alcohol develop corresponding hyperalgesia. Olfactory cues mediate the transfer of hyperalgesia to the bystander mice, which can be measured using mechanical, thermal, and chemical tests. Hyperalgesia in bystanders does not co-occur with anxiety or changes in corticosterone and cannot be explained by visually dependent emotional contagion or stress-induced hyperalgesia. These experiments reveal the multifaceted relationship between the social environment and pain behavior and support the use of mice as a model system for investigating these factors. In addition, these experiments highlight the need for proper consideration of how experimental animals are housed and tested.
Keywords: Chronic pain; alcohol withdrawal; empathy; olfactory communication; social environment.
Figures
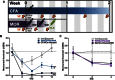
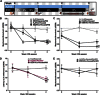
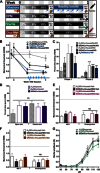
References
-
- Hadjistavropoulos T., Craig K. D., Duck S., Cano A., Goubert L., Jackson P. L., Mogil J. S., Rainville P., Sullivan M. J. L., de C Williams A. C., Vervoort T., Fitzgerald T. D., A biopsychosocial formulation of pain communication. Psychol. Bull. 137, 910–939 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Loggia M. L., Mogil J. S., Bushnell C. M., Empathy hurts: Compassion for another increases both sensory and affective components of pain perception. Pain 136, 168–176 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Fanselow M. S., Odors released by stressed rats produce opioid analgesia in unstressed rats. Behav. Neurosci. 99, 589–600 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Raber P., Devor M., Social variables affect phenotype in the neuroma model of neuropathic pain. Pain 97, 139–150 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

