Human CaaX protease ZMPSTE24 expressed in yeast: Structure and inhibition by HIV protease inhibitors
- PMID: 27774687
- PMCID: PMC5275749
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3074
Human CaaX protease ZMPSTE24 expressed in yeast: Structure and inhibition by HIV protease inhibitors
Abstract
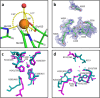
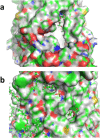
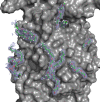
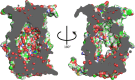
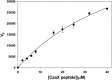
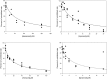
The function and localization of proteins and peptides containing C-terminal "CaaX" (Cys-aliphatic-aliphatic-anything) sequence motifs are modulated by post-translational attachment of isoprenyl groups to the cysteine sulfhydryl, followed by proteolytic cleavage of the aaX amino acids. The zinc metalloprotease ZMPSTE24 is one of two enzymes known to catalyze this cleavage. The only identified target of mammalian ZMPSTE24 is prelamin A, the precursor to the nuclear scaffold protein lamin A. ZMPSTE24 also cleaves prelamin A at a second site 15 residues upstream from the CaaX site. Mutations in ZMPSTE24 result in premature-aging diseases and inhibition of ZMPSTE24 activity has been reported to be an off-target effect of HIV protease inhibitors. We report here the expression (in yeast), purification, and crystallization of human ZMPSTE24 allowing determination of the structure to 2.0 Å resolution. Compared to previous lower resolution structures, the enhanced resolution provides: (1) a detailed view of the active site of ZMPSTE24, including water coordinating the catalytic zinc; (2) enhanced visualization of fenestrations providing access from the exterior to the interior cavity of the protein; (3) a view of the C-terminus extending away from the main body of the protein; (4) localization of ordered lipid and detergent molecules at internal and external surfaces and also projecting through fenestrations; (5) identification of water molecules associated with the surface of the internal cavity. We also used a fluorogenic assay of the activity of purified ZMPSTE24 to demonstrate that HIV protease inhibitors directly inhibit the human enzyme in a manner indicative of a competitive mechanism.
Keywords: CaaX protease; HIV protease inhibitor; Isoprenoid; X-ray crystallography; ZMPSTE24; enzyme inhibitor; membrane protein; metalloprotease; progeria; zinc.
© 2016 The Protein Society.
Figures

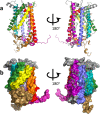
Similar articles
-
Site specificity determinants for prelamin A cleavage by the zinc metalloprotease ZMPSTE24.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100165. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015792. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33293369 Free PMC article.
-
ZMPSTE24 missense mutations that cause progeroid diseases decrease prelamin A cleavage activity and/or protein stability.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Jul 13;11(7):dmm033670. doi: 10.1242/dmm.033670. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29794150 Free PMC article.
-
A Quantitative FRET Assay for the Upstream Cleavage Activity of the Integral Membrane Proteases Human ZMPSTE24 and Yeast Ste24.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2009:279-293. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9532-5_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31152411
-
A humanized yeast system to analyze cleavage of prelamin A by ZMPSTE24.Methods. 2019 Mar 15;157:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Methods. 2019. PMID: 30625386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZMPSTE24, an integral membrane zinc metalloprotease with a connection to progeroid disorders.Biol Chem. 2009 Aug;390(8):761-73. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.080. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19453269 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoramidon inhibits the integral membrane protein zinc metalloprotease ZMPSTE24.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Aug 1;74(Pt 8):739-747. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318003431. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30082509 Free PMC article.
-
ZMPSTE24 Is Associated with Elevated Inflammation and Progerin mRNA.Cells. 2020 Aug 28;9(9):1981. doi: 10.3390/cells9091981. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32872320 Free PMC article.
-
Prelamin A and ZMPSTE24 in premature and physiological aging.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2270345. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2270345. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 37885131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ste24: An Integral Membrane Protein Zinc Metalloprotease with Provocative Structure and Emergent Biology.J Mol Biol. 2020 Aug 21;432(18):5079-5090. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.03.016. Epub 2020 Mar 19. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32199981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Factors and Pathways of Hepatotoxicity Associated with HIV/SARS-CoV-2 Protease Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 27;24(9):7938. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097938. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175645 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrowman J, Michaelis S (2009) ZMPSTE24, an integral membrane zinc metalloprotease with a connection to progeroid disorders. Biol Chem 390:761–773. - PubMed
-
- Pendas AM, Zhou Z, Cadinanos J, Freije JM, Wang J, Hultenby K, Astudillo A, Wernerson A, Rodriguez F, Tryggvason K, Lopez‐Otin C (2002) Defective prelamin A processing and muscular and adipocyte alterations in Zmpste24 metalloproteinase‐deficient mice. Nat Genet 31:94–99. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Fryns JP, Auchus RJ, Garg A (2003) Zinc metalloproteinase, ZMPSTE24, is mutated in mandibuloacral dysplasia. Hum Mol Genet 12:1995–2001. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

