Psychopathology in 7-year-old children: Differences in maternal and paternal ratings and the genetic epidemiology
- PMID: 27774759
- PMCID: PMC5413051
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32500
Psychopathology in 7-year-old children: Differences in maternal and paternal ratings and the genetic epidemiology
Abstract
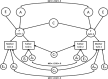
The assessment of children's psychopathology is often based on parental report. Earlier studies have suggested that rater bias can affect the estimates of genetic, shared environmental and unique environmental influences on differences between children. The availability of a large dataset of maternal as well as paternal ratings of psychopathology in 7-year old children enabled (i) the analysis of informant effects on these assessments, and (ii) to obtain more reliable estimates of the genetic and non-genetic effects. DSM-oriented measures of affective, anxiety, somatic, attention-deficit/hyperactivity, oppositional-defiant, conduct, and obsessive-compulsive problems were rated for 12,310 twin pairs from the Netherlands Twin Register by mothers (N = 12,085) and fathers (N = 8,516). The effects of genetic and non-genetic effects were estimated on the common and rater-specific variance. For all scales, mean scores on maternal ratings exceeded paternal ratings. Parents largely agreed on the ranking of their child's problems (r 0.60-0.75). The heritability was estimated over 55% for maternal and paternal ratings for all scales, except for conduct problems (44-46%). Unbiased shared environmental influences, i.e., on the common variance, were significant for affective (13%), oppositional (13%), and conduct problems (37%). In clinical settings, different cutoffs for (sub)clinical scores could be applied to paternal and maternal ratings of their child's psychopathology. Only for conduct problems, shared environmental and genetic influences explain an equal amount in differences between children. For the other scales, genetic factors explain the majority of the variance, especially for the common part that is free of rater bias. © 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: parental ratings; psychopathology; rater bias; shared environment; twins.
© 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heritability of Behavioral Problems in 7-Year Olds Based on Shared and Unique Aspects of Parental Views.Behav Genet. 2017 Mar;47(2):152-163. doi: 10.1007/s10519-016-9823-1. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Behav Genet. 2017. PMID: 27796610 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics and developmental psychopathology: 2. The main effects of genes and environment on behavioral problems in the Virginia Twin Study of Adolescent Behavioral Development.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1997 Nov;38(8):965-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01614.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1997. PMID: 9413795
-
Genetic and environmental influences on Anxious/Depression during childhood: a study from the Netherlands Twin Register.Genes Brain Behav. 2005 Nov;4(8):466-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2005.00141.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2005. PMID: 16268991 Clinical Trial.
-
Genetic and environmental stability in attention problems across the lifespan: evidence from the Netherlands twin register.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013 Jan;52(1):12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23265630 Review.
-
The inclusion of fathers in the empirical investigation of child psychopathology: an update.J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2006 Dec;35(4):583-9. doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp3504_10. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2006. PMID: 17007604 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic influences on externalizing psychopathology overlap with cognitive functioning and show developmental variation.Eur Psychiatry. 2021 Mar 31;64(1):e29. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2021.21. Eur Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33785081 Free PMC article.
-
Do environmental effects indexed by parental genetic variation influence common psychiatric symptoms in childhood?Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Mar 18;13(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02348-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36934099 Free PMC article.
-
Examining Maternal Elaborative Reminiscing as a Protective Factor in the Intergenerational Transmission of Psychopathology.Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2021 Aug;49(8):989-999. doi: 10.1007/s10802-021-00790-4. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol. 2021. PMID: 33646481
-
Genetic and environmental influences on conduct and antisocial personality problems in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;27(9):1123-1132. doi: 10.1007/s00787-017-1014-y. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28638947 Free PMC article.
-
Association between maternal employment and the child´s mental health: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024 Sep;33(9):3025-3042. doi: 10.1007/s00787-023-02164-1. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 36780025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdellaoui A, Bartels M, Hudziak JJ, Rizzu P, van Beijsterveldt TC, Boomsma DI. 2008. Genetic influences on thought problems in 7‐year‐olds: A twin‐study of genetic, environmental and rater effects. Twin Res Hum Genet 11(6):571–578. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach TM, Mcconaughy SH, Howell CT. 1987. Child adolescent behavioral and emotional‐problems—implications of cross‐informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychol Bull 101(2):213–232. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla L. 2001. Manual for the ASEBA school‐age forms & profiles: An integrated system of multi‐informant assessment. Burlington, VT: ASEBA. xii, p 238.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. 2000. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed, text rev ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Andersen PAS, Bilenberg N. 2012. Comparison of child behavior checklist subscales in screening for obsessive‐compulsive disorder. Dan Med J 59(11):1–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

