Neurobiochemical changes in the vicinity of a nanostructured neural implant
- PMID: 27775024
- PMCID: PMC5075914
- DOI: 10.1038/srep35944
Neurobiochemical changes in the vicinity of a nanostructured neural implant
Abstract
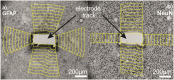
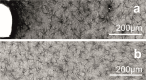
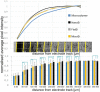
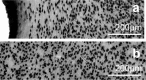
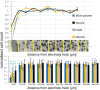
Neural interface technologies including recording and stimulation electrodes are currently in the early phase of clinical trials aiming to help patients with spinal cord injuries, degenerative disorders, strokes interrupting descending motor pathways, or limb amputations. Their lifetime is of key importance; however, it is limited by the foreign body response of the tissue causing the loss of neurons and a reactive astrogliosis around the implant surface. Improving the biocompatibility of implant surfaces, especially promoting neuronal attachment and regeneration is therefore essential. In our work, bioactive properties of implanted black polySi nanostructured surfaces (520-800 nm long nanopillars with a diameter of 150-200 nm) were investigated and compared to microstructured Si surfaces in eight-week-long in vivo experiments. Glial encapsulation and local neuronal cell loss were characterised using GFAP and NeuN immunostaining respectively, followed by systematic image analysis. Regarding the severity of gliosis, no significant difference was observed in the vicinity of the different implant surfaces, however, the number of surviving neurons close to the nanostructured surface was higher than that of the microstructured ones. Our results imply that the functionality of implanted microelectrodes covered by Si nanopillars may lead to improved long-term recordings.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanoscale laminin coating modulates cortical scarring response around implanted silicon microelectrode arrays.J Neural Eng. 2006 Dec;3(4):316-26. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/3/4/009. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Neural Eng. 2006. PMID: 17124336
-
Bioactive properties of nanostructured porous silicon for enhancing electrode to neuron interfaces.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18(10):1263-81. doi: 10.1163/156856207782177882. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007. PMID: 17939885
-
Seeding neural progenitor cells on silicon-based neural probes.J Neurosurg. 2010 Sep;113(3):673-81. doi: 10.3171/2010.1.JNS09313. J Neurosurg. 2010. PMID: 20151783
-
Macrophage responses to implants: prospects for personalized medicine.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Dec;98(6):953-62. doi: 10.1189/jlb.5VMR0415-166R. Epub 2015 Jul 13. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26168797 Review.
-
Biocompatibility screening in cardiovascular implants.Z Kardiol. 2005 Jun;94(6):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s00392-005-0231-4. Z Kardiol. 2005. PMID: 15940438 Review.
Cited by
-
ECAP growth function to increasing pulse amplitude or pulse duration demonstrates large inter-animal variability that is reflected in auditory cortex of the guinea pig.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 2;13(8):e0201771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201771. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30071005 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistological responses in mice implanted with Parylene HT - ITO ECoG devices.Front Neurosci. 2023 Aug 31;17:1209913. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1209913. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37746144 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro-Nano Interfaces: Utilizing Nano-Coatings and Nanoparticles to Enable Next-Generation Electrophysiological Recording, Neural Stimulation, and Biochemical Modulation.Adv Funct Mater. 2018 Mar 21;28(12):1700239. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201700239. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Adv Funct Mater. 2018. PMID: 33867903 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical and biological performance of hierarchical platinum-iridium electrodes structured by a femtosecond laser.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2022 Sep 2;8:96. doi: 10.1038/s41378-022-00433-8. eCollection 2022. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2022. PMID: 36065436 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Review of Microelectrode Arrays and Strategies for Improving Neural Interfaces.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Oct;8(19):e1900558. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201900558. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 31464094 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

