CD133+ brain tumor-initiating cells are dependent on STAT3 signaling to drive medulloblastoma recurrence
- PMID: 27775079
- PMCID: PMC5541269
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.235
CD133+ brain tumor-initiating cells are dependent on STAT3 signaling to drive medulloblastoma recurrence
Abstract
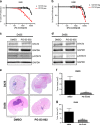
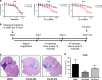
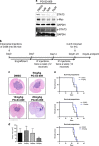
Medulloblastoma (MB), the most common malignant paediatric brain tumor, is currently treated using a combination of surgery, craniospinal radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Owing to MB stem cells (MBSCs), a subset of MB patients remains untreatable despite standard therapy. CD133 is used to identify MBSCs although its functional role in tumorigenesis has yet to be determined. In this work, we showed enrichment of CD133 in Group 3 MB is associated with increased rate of metastasis and poor clinical outcome. The signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 (STAT3) pathway are selectively activated in CD133+ MBSCs and promote tumorigenesis through regulation of c-MYC, a key genetic driver of Group 3 MB. We screened compound libraries for STAT3 inhibitors and treatment with the selected STAT3 inhibitors resulted in tumor size reduction in vivo. We propose that inhibition of STAT3 signaling in MBSCs may represent a potential therapeutic strategy to treat patients with recurrent MB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gajjar A, Chintagumpala M, Ashley D, Kellie S, Kun LE, Merchant TE et al. Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol 2006; 7: 813–820. - PubMed
-
- Mabbott DJ, Spiegler BJ, Greenberg ML, Rutka JT, Hyder DJ, Bouffet E. Serial evaluation of academic and behavioral outcome after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 2256–2263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

