RNA modification in Cajal bodies
- PMID: 27775477
- PMCID: PMC5519239
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1249091
RNA modification in Cajal bodies
Abstract
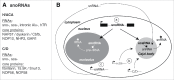
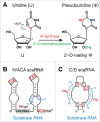
Aside from nucleoli, Cajal bodies (CBs) are the best-characterized organelles of mammalian cell nuclei. Like nucleoli, CBs concentrate ribonucleoproteins (RNPs), in particular, spliceosomal small nuclear RNPs (snRNPs) and small nucleolar RNPs (snoRNPs). In one of the best-defined functions of CBs, most of the snoRNPs are involved in site-specific modification of snRNAs. The two major modifications are pseudouridylation and 2'-O-methylation that are guided by the box H/ACA and C/D snoRNPs, respectively. This review details the modifications, their function, the mechanism of modification, and the machineries involved. We dissect the different classes of noncoding RNAs that meet in CBs, guides and substrates. Open questions and conundrums, often raised and appearing due to experimental limitations, are pointed out and discussed. The emphasis of the review is on mammalian CBs and their function in modification of noncoding RNAs.
Keywords: 2′-O-methyl; C/D RNA; Cajal body; H/ACA RNA; pseudouridine; scaRNA; snRNA; snoRNA; spliceosomal; telomerase.
Figures
References
-
- Agris PF. The importance of being modified: roles of modified nucleosides and Mg2+ in RNA structure and function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 1996; 53:79-129; PMID:8650309; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60143-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrade LE, Chan EK, Raska I, Peebles CL, Roos G, Tan EM. Human autoantibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. J Exp Med 1991; 173:1407-19; PMID:2033369; https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.173.6.1407 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrade LE, Tan EM, Chan EK. Immunocytochemical analysis of the coiled body in the cell cycle and during cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90:1947-51; PMID:8446613; https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.5.1947 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnez JG, Steitz TA. Crystal structure of unmodified tRNA(Gln) complexed with glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase and ATP suggests a possible role for pseudo-uridines in stabilization of RNA structure. Biochemistry 1994; 33:7560-67; PMID:8011621; https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00190a008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Auffinger P, Westhof E. Rules governing the orientation of the 2′-hydroxyl group in RNA. J Mol Biol 1997; 274:54-63; PMID:9398515; https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.1370 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
