Systematic Analysis of the 4-Coumarate:Coenzyme A Ligase (4CL) Related Genes and Expression Profiling during Fruit Development in the Chinese Pear
- PMID: 27775579
- PMCID: PMC5083928
- DOI: 10.3390/genes7100089
Systematic Analysis of the 4-Coumarate:Coenzyme A Ligase (4CL) Related Genes and Expression Profiling during Fruit Development in the Chinese Pear
Abstract
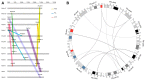
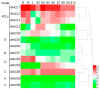
In plants, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligases (4CLs), comprising some of the adenylate-forming enzymes, are key enzymes involved in regulating lignin metabolism and the biosynthesis of flavonoids and other secondary metabolites. Although several 4CL-related proteins were shown to play roles in secondary metabolism, no comprehensive study on 4CL-related genes in the pear and other Rosaceae species has been reported. In this study, we identified 4CL-related genes in the apple, peach, yangmei, and pear genomes using DNATOOLS software and inferred their evolutionary relationships using phylogenetic analysis, collinearity analysis, conserved motif analysis, and structure analysis. A total of 149 4CL-related genes in four Rosaceous species (pear, apple, peach, and yangmei) were identified, with 30 members in the pear. We explored the functions of several 4CL and acyl-coenzyme A synthetase (ACS) genes during the development of pear fruit by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). We found that duplication events had occurred in the 30 4CL-related genes in the pear. These duplicated 4CL-related genes are distributed unevenly across all pear chromosomes except chromosomes 4, 8, 11, and 12. The results of this study provide a basis for further investigation of both the functions and evolutionary history of 4CL-related genes.
Keywords: 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligases (4CL); acyl-coenzyme A synthetase (ACS); gene family; pear; qRT-PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Tyler B. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa. Science. 2006;313:1596–1604. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

