PIM1 kinase regulates cell death, tumor growth and chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 27775704
- PMCID: PMC5552044
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4198
PIM1 kinase regulates cell death, tumor growth and chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum: PIM1 kinase regulates cell death, tumor growth and chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer.Nat Med. 2017 Apr 7;23(4):526. doi: 10.1038/nm0417-526c. Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28388604 No abstract available.
-
Erratum: PIM1 kinase regulates cell death, tumor growth and chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer.Nat Med. 2017 Jun 6;23(6):788. doi: 10.1038/nm0617-788b. Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 28586336 No abstract available.
Abstract
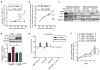
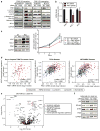
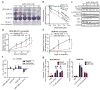
Triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) have poor prognosis and lack targeted therapies. Here we identified increased copy number and expression of the PIM1 proto-oncogene in genomic data sets of patients with TNBC. TNBC cells, but not nonmalignant mammary epithelial cells, were dependent on PIM1 for proliferation and protection from apoptosis. PIM1 knockdown reduced expression of the anti-apoptotic factor BCL2, and dynamic BH3 profiling of apoptotic priming revealed that PIM1 prevents mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in TNBC cell lines. In TNBC tumors and their cellular models, PIM1 expression was associated with several transcriptional signatures involving the transcription factor MYC, and PIM1 depletion in TNBC cell lines decreased, in a MYC-dependent manner, cell population growth and expression of the MYC target gene MCL1. Treatment with the pan-PIM kinase inhibitor AZD1208 impaired the growth of both cell line and patient-derived xenografts and sensitized them to standard-of-care chemotherapy. This work identifies PIM1 as a malignant-cell-selective target in TNBC and the potential use of PIM1 inhibitors for sensitizing TNBC to chemotherapy-induced apoptotic cell death.
Figures



References
-
- Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008;52:108–118. - PubMed
-
- Symmans WF, et al. Measurement of residual breast cancer burden to predict survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25:4414–4422. - PubMed
-
- Labisso WL, et al. MYC directs transcription of MCL1 and eIF4E genes to control sensitivity of gastric cancer cells toward HDAC inhibitors. Cell cycle. 2012;11:1593–1602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

