Epigenetic regulation of estrogen receptor α contributes to age-related differences in transcription across the hippocampal regions CA1 and CA3
- PMID: 27776265
- PMCID: PMC5479492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.09.013
Epigenetic regulation of estrogen receptor α contributes to age-related differences in transcription across the hippocampal regions CA1 and CA3
Abstract
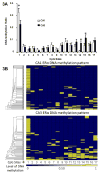
The expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) varies across brain regions and changes with age and according to the previous history of estradiol exposure. ERα is regulated by a number of mechanisms including the level of mRNA (Esr1) expression. For this study, we took advantage of regional differences in hippocampal ERα expression to investigate DNA ERα promoter methylation at CpG dinucleotide sites as a potential epigenetic mechanism for regulating gene expression. Young and aged female Fischer 344 rats were ovariectomized, and Esr1 expression and ERα promoter methylation were examined in hippocampal regions CA1 and CA3, either 3 or 14 weeks following surgery. The results indicate that reduced Esr1 expression in region CA1 relative to CA3 was associated with an increase in DNA methylation in region CA1, particularly for the first CpG site. Additionally, differential methylation of distal CpG sites, 11-17, was associated with altered Esr1 expression during aging or following long-term hormone deprivation. The results support the idea that methylation of site 1 may be the primary regulatory region for cross-regional patterns in ERα expression, while distal sites are modifiable across the life span and may act as a feedback mechanism for ERα activity.
Keywords: Aging; DNA methylation; Estrogen receptor alpha; Hippocampus; Transcription.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors disclose that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest including any financial, and personal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential ESR1 Promoter Methylation in the Peripheral Blood-Findings from the Women 40+ Healthy Aging Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 21;21(10):3654. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103654. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455834 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of estrogen receptors in two hippocampal regions during the estrous cycle of the rat.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011 Nov;294(11):1913-9. doi: 10.1002/ar.21247. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21972199
-
Epigenetic disruption of estrogen receptor alpha is induced by a glyphosate-based herbicide in the preimplantation uterus of rats.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019 Jan 15;480:133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30391669
-
Estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression in the cortex: sex differences during development and in adulthood.Horm Behav. 2011 Mar;59(3):353-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.08.004. Epub 2010 Aug 14. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 20713055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of oestrogen receptor gene expression: new insights and novel mechanisms.J Neuroendocrinol. 2009 Mar;21(4):238-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01830.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19207817 Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep and Methylation of Estrogen Receptor Genes, ESR1 and GPER, in Healthy Middle-Aged and Older Women: Findings from the Women 40+ Healthy Aging Study.Nat Sci Sleep. 2020 Jul 27;12:525-536. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S256102. eCollection 2020. Nat Sci Sleep. 2020. PMID: 32801978 Free PMC article.
-
Differential ESR1 Promoter Methylation in the Peripheral Blood-Findings from the Women 40+ Healthy Aging Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 21;21(10):3654. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103654. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455834 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis of canine brain morphometry links tumour risk to oestrogen deficiency and accelerated brain ageing.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 29;9(1):12506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48446-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31467332 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation of Synaptic Genes in the Prefrontal Cortex Is Associated with Aging and Age-Related Cognitive Impairment.Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Aug 2;9:249. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00249. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28824413 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase 2 Inhibition Attenuates Downregulation of Hippocampal Plasticity Gene Expression during Aging.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2432-2442. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0490-x. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28364391
References
-
- Bicaku E, Marchion DC, Schmitt ML, Munster PN. Selective inhibition of histone deacetylase 2 silences progesterone receptor-mediated signaling. Cancer Res. 2008;68(5):1513–1519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

