Impact of acute kidney injury on renal allograft survival
- PMID: 27776444
- PMCID: PMC6014363
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2016.1244076
Impact of acute kidney injury on renal allograft survival
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the major determinants of graft survival in kidney transplantation (KTx). Renal Transplant recipients are more vulnerable to develop AKI than general population. AKI in the transplant recipient differs from community acquired, in terms of risk factors, etiology and outcome. Our aim was to study the incidence, risk factors, etiology, outcome and the impact of AKI on graft survival.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 219 renal transplant recipients (both live and deceased donor) was done.
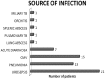
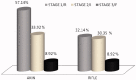
Results: AKI was observed in 112 (51.14%) recipients, with mean age of 41.5 ± 11.2 years during follow-up of 43.2 ± 12.5 months. Etiologies of AKI were infection (47.32%), rejection (26.78%), calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) toxicity (13.39%), and recurrence of native kidney disease (NKD) (4.46%). New Onset Diabetes After Transplant (NODAT) and deceased donor transplant were the significant risk factors for AKI. During follow-up 70.53% (p = .004) of AKI recipients progressed to chronic kidney disease (CKD) in contrast to only 11.21% (p = .342) of non AKI recipients. Risk factors for CKD were AKI within first year of transplant (HR: 7.32, 95%CI: 4.37-15.32, p = .007), multiple episodes of AKI (HR: 6.92, 95%CI: 3.92-9.63, p = .008), infection (HR: 3.62, 95%CI: 2.8-5.75, p = .03) and rejection (HR: 9.92 95%CI: 5.56-12.36, p = .001).
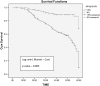
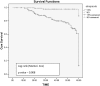
Conclusion: Renal transplant recipients have high risk for AKI and it hampers long-term graft survival.
Keywords: AKI; CKD; graft survival; hemodialysis; kidney transplant.
Figures
References
-
- Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, et al. Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: A comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1292–1298. - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Malhotra HS, Sakhuja V, Chugh KS.. Spectrum of hospital-acquired acute renal failure in the developing countries: Chandigarh study. Q J Med. 1992;83:497–505. - PubMed
-
- Jayakumar M, Prabahar MR, Fernando EM, Manorajan R, Venkatraman R, Balaraman V. Epidemiologic trend changes in acute renal failure: A tertiary center experience from South India. Ren Fail. 2006;28:405–410. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury March 2012; Section 2, chapter 2.1, volume 2, issue1. Available at: http:/www.kidneyinternational.org.
-
- KDIGO 2012 Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease January 2013; volume 3, issue 1, chapter 1. Available at: http://www.kidney-international.org. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical