The incidence of increased ICP in ICU patients with non-traumatic coma as diagnosed by ONSD and CT: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 27776491
- PMCID: PMC5078918
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-016-0267-1
The incidence of increased ICP in ICU patients with non-traumatic coma as diagnosed by ONSD and CT: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
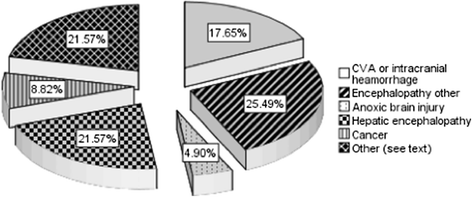
Background: Unexplained coma after critical illness can be multifactorial. We evaluated the diagnostic ability of bedside Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter [ONSD] as a screening test for non-traumatic radiographic cerebral edema.
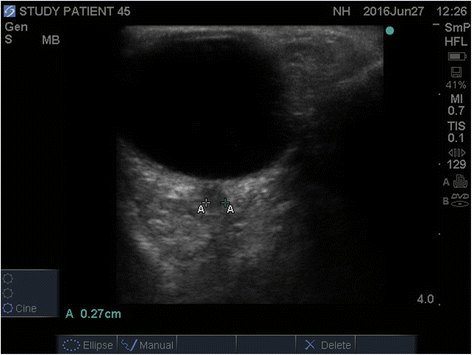
Methods: In a prospective study, mixed medical-surgical intensive care units [ICU] patients with non-traumatic coma [GCS < 9] underwent bedside ultrasonographic ONSD measurements. Non-traumatic radiographic cerebral edema [NTRCE] was defined as > 5 mm midline shift, cisternal, sulcal effacement, or hydrocephalus on CT.
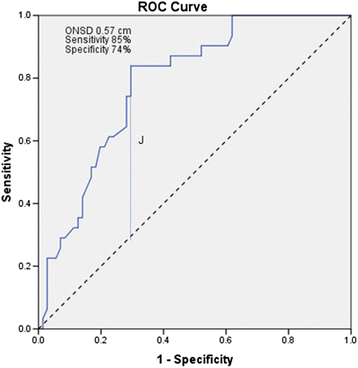
Results: NTRCE was identified in 31 of 102 patients [30.4 %]. The area under the ROC curve for detecting radiographic edema by ONSD was 0.785 [95 % CI 0.695-0.874, p <0.001]. ONSD diameter of 0.57 cm was found to be the best cutoff threshold with a sensitivity 84 % and specificity 71 %, AUC 0.785 [95 % CI 0.695-0.874, p <0.001]. Using ONSD as a bedside test increased the post-test odds ratio [OR] for NTRCE by 2.89 times [positive likelihood ratio], whereas post-test OR for NTRCE decreased markedly given a negative ONSD test [ONSD measurement less than 0.57 cm]; negative likelihood ratio 0.22.
Conclusions: The use of ONSD as a bedside test in patients with non-traumatic coma has diagnostic value in identifying patients with non-traumatic radiographic cerebral edema.
Keywords: Coma; Critical illness; Non-traumatic radiographic cerebral edema; Optic nerve sheath diameter.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

