Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib attenuates joint contracture following immobilization in rat knees
- PMID: 27776498
- PMCID: PMC5078937
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1303-5
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib attenuates joint contracture following immobilization in rat knees
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to clarify the following two points: First, whether a cyclooxygenase-2 mediated pathway is involved in the formation of immobilization-induced joint contracture and, second, the effectiveness of oral administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib (CBX) for the prevention of myogenic and arthrogenic contracture following immobilization in a rat model.
Methods: Thirty male rats were randomly divided into three groups: immobilization (Im), Im + CBX, and control (n = 10 each). External fixation immobilized the right knee joint of Im and Im + CBX groups in flexion for 3 weeks. 50 mg/kg of CBX was administrated daily to the Im + CBX group during this period. The passive range of motion (ROM) of knee joints was measured before and after transection of knee flexor muscles and myogenic and arthrogenic ROM restrictions were calculated. The semitendinosus muscles and knee joints were investigated histologically to elucidate factors responsible for contracture.
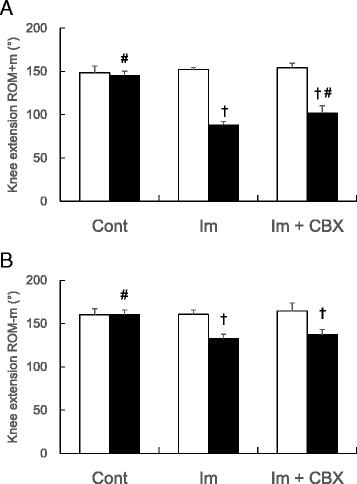
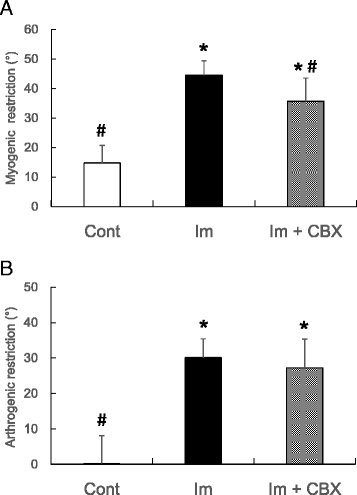
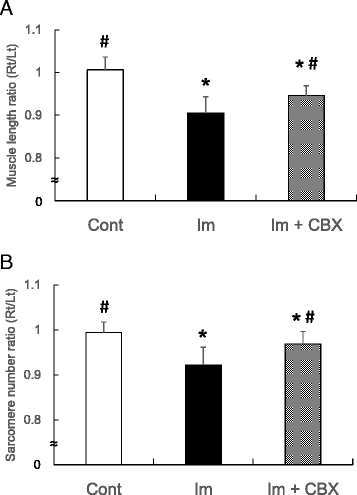
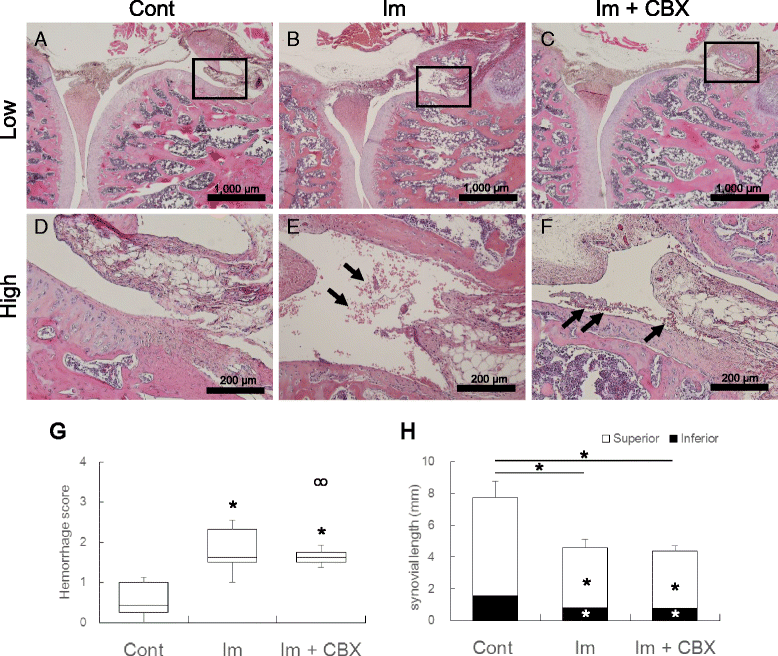
Results: Myogenic ROM restrictions were exhibited both in Im and Im + CBX groups (44 ± 5 and 36 ± 8 °, respectively), but restrictions significantly decreased in the Im + CBX group compared to the Im group. Significant reductions of the muscle length ratios (Rt/Lt) and sarcomere number ratios (Rt/Lt) in knee flexor semitendinosus muscle, which are responsible for myogenic contracture, were also seen both in Im group (92 ± 5 and 92 ± 4 %, respectively) and Im + CBX group (97 ± 3 and 97 ± 3 %, respectively), but were inhibited by CBX administration (P < 0.05). Im and Im + CBX groups exhibited arthrogenic ROM restrictions with no significant differences (82 ± 3 and 83 ± 5 °, respectively). Posterior synovial length shortening and pathological changes (hemorrhage in joint cavities and capsule edema) in the knee joints were comparable between Im and Im + CBX groups.
Conclusions: Oral administration of celecoxib partially reduced myogenic ROM restriction concomitantly with knee flexor muscle shortening following immobilization. These results imply that inflammation and nociception are involved in myogenic contracture formation independently of joint immobilization, and that CBX is effective in preventing joint contracture following immobilization in rats.
Keywords: Celecoxib; Immobilization; Joint contracture; Knee; Muscle.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammation and Fibrosis Induced by Joint Remobilization, and Relevance to Progression of Arthrogenic Joint Contracture: A Narrative Review.Physiol Res. 2022 Aug 31;71(4):447-488. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934876. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35770468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active exercise on immobilization-induced contractured rat knees develops arthrogenic joint contracture with pathological changes.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018 Feb 1;124(2):291-301. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00438.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018. PMID: 28982941
-
Anti-inflammatory Drug Dexamethasone Treatment During the Remobilization Period Improves Range of Motion in a Rat Knee Model of Joint Contracture.Inflammation. 2018 Aug;41(4):1409-1423. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0788-5. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29911276
-
Development of arthrogenic joint contracture as a result of pathological changes in remobilized rat knees.J Orthop Res. 2017 Jul;35(7):1414-1423. doi: 10.1002/jor.23419. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Orthop Res. 2017. PMID: 27601089
-
The mechanisms and treatments of muscular pathological changes in immobilization-induced joint contracture: A literature review.Chin J Traumatol. 2019 Apr;22(2):93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.02.001. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Chin J Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30928194 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy Prevents Treadmill Exercise-Induced Progression of Arthrogenic Joint Contracture Via Attenuation of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Remobilized Rat Knees.Inflammation. 2019 Jun;42(3):857-873. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0941-1. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30506108
-
Low-level laser therapy attenuates arthrogenic contracture induced by anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery in rats.Physiol Res. 2022 Jul 29;71(3):389-399. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934796. Epub 2022 May 26. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35616040 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of losartan and atorvastatin on the development of early posttraumatic joint stiffness in a rat model.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Jul 30;13:2603-2618. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S204135. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31440039 Free PMC article.
-
A novel rat model of stable posttraumatic joint stiffness of the knee.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 Jul 25;13(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0894-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 30045767 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Fibrosis Induced by Joint Remobilization, and Relevance to Progression of Arthrogenic Joint Contracture: A Narrative Review.Physiol Res. 2022 Aug 31;71(4):447-488. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934876. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35770468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

