Dose-dependent white matter damage after brain radiotherapy
- PMID: 27776747
- PMCID: PMC5136508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.10.003
Dose-dependent white matter damage after brain radiotherapy
Abstract
Background and purpose: Brain radiotherapy is limited in part by damage to white matter, contributing to neurocognitive decline. We utilized diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) with multiple b-values (diffusion weightings) to model the dose-dependency and time course of radiation effects on white matter.
Materials and methods: Fifteen patients with high-grade gliomas treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy underwent MRI with DTI prior to radiotherapy, and after months 1, 4-6, and 9-11. Diffusion tensors were calculated using three weightings (high, standard, and low b-values) and maps of fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (λ∥), and radial diffusivity (λ⊥) were generated. The region of interest was all white matter.
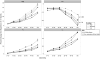
Results: MD, λ∥, and λ⊥ increased significantly with time and dose, with corresponding decrease in FA. Greater changes were seen at lower b-values, except for FA. Time-dose interactions were highly significant at 4-6months and beyond (p<.001), and the difference in dose response between high and low b-values reached statistical significance at 9-11months for MD, λ∥, and λ⊥ (p<.001, p<.001, p=.005 respectively) as well as at 4-6months for λ∥ (p=.04).
Conclusions: We detected dose-dependent changes across all doses, even <10Gy. Greater changes were observed at low b-values, suggesting prominent extracellular changes possibly due to vascular permeability and neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; MRI; Radiation; Radiotherapy; White matter; b-Value.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, Neuwelt EA. Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation-induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:627–42. - PubMed
-
- Frost M, Sloan J. Quality of life measurements: A soft outcome - Or is it? Am J Manag Care. 2002;8:S574–9. - PubMed
-
- Haris M, Kumar S, Raj MK, et al. Serial diffusion tensor imaging to characterize radiation-induced changes in normal-appearing white matter following radiotherapy in patients with adult low-grade gliomas. Radiat Med - Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2008;26:140–50. doi: 10.1007/s11604-007-0209-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

