Structural Analysis of the Catalytic Mechanism and Substrate Specificity of Anabaena Alkaline Invertase InvA Reveals a Novel Glucosidase
- PMID: 27777307
- PMCID: PMC5207263
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.759290
Structural Analysis of the Catalytic Mechanism and Substrate Specificity of Anabaena Alkaline Invertase InvA Reveals a Novel Glucosidase
Abstract
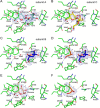
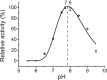
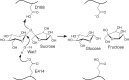
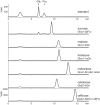
Invertases catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose to glucose and fructose, thereby playing a key role in primary metabolism and plant development. According to the optimum pH, invertases are classified into acid invertases (Ac-Invs) and alkaline/neutral invertases (A/N-Invs), which share no sequence homology. Compared with Ac-Invs that have been extensively studied, the structure and catalytic mechanism of A/N-Invs remain unknown. Here we report the crystal structures of Anabaena alkaline invertase InvA, which was proposed to be the ancestor of modern plant A/N-Invs. These structures are the first in the GH100 family. InvA exists as a hexamer in both crystal and solution. Each subunit consists of an (α/α)6 barrel core structure in addition to an insertion of three helices. A couple of structures in complex with the substrate or products enabled us to assign the subsites -1 and +1 specifically binding glucose and fructose, respectively. Structural comparison combined with enzymatic assays indicated that Asp-188 and Glu-414 are putative catalytic residues. Further analysis of the substrate binding pocket demonstrated that InvA possesses a stringent substrate specificity toward the α1,2-glycosidic bond of sucrose. Together, we suggest that InvA and homologs represent a novel family of glucosidases.
Keywords: GH100; alkaline/neutral invertases; crystal structure; cyanobacteria; enzyme catalysis; glucosidase; glycoside hydrolase; substrate specificity; sucrose metabolism.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Vargas W. A., and Salerno G. L. (2010) The Cinderella story of sucrose hydrolysis: alkaline/neutral invertases, from cyanobacteria to unforeseen roles in plant cytosol and organelles. Plant Sci. 178, 1–8
-
- Ruan Y.-L., Jin Y., Yang Y.-J., Li G.-J., and Boyer J. S. (2010) Sugar input, metabolism, and signaling mediated by invertase: roles in development, yield potential, and response to drought and heat. Mol. Plant 3, 942–955 - PubMed
-
- Koch K. (2004) Sucrose metabolism: regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7, 235–246 - PubMed
-
- Salerno G. L., and Curatti L. (2003) Origin of sucrose metabolism in higher plants: when, how, and why? Trends Plant Sci. 8, 63–69 - PubMed
-
- Ruan Y.-L. (2014) Sucrose metabolism: gateway to diverse carbon use and sugar signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 65, 33–67 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

