Air pollution, epigenetics, and asthma
- PMID: 27777592
- PMCID: PMC5069789
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-016-0159-4
Air pollution, epigenetics, and asthma
Abstract
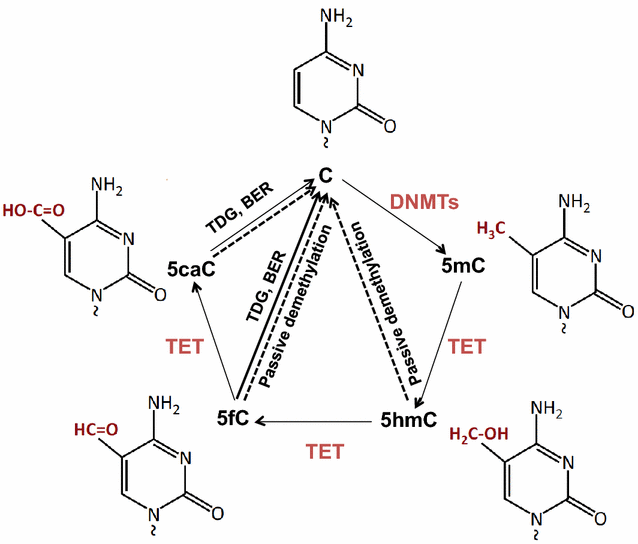
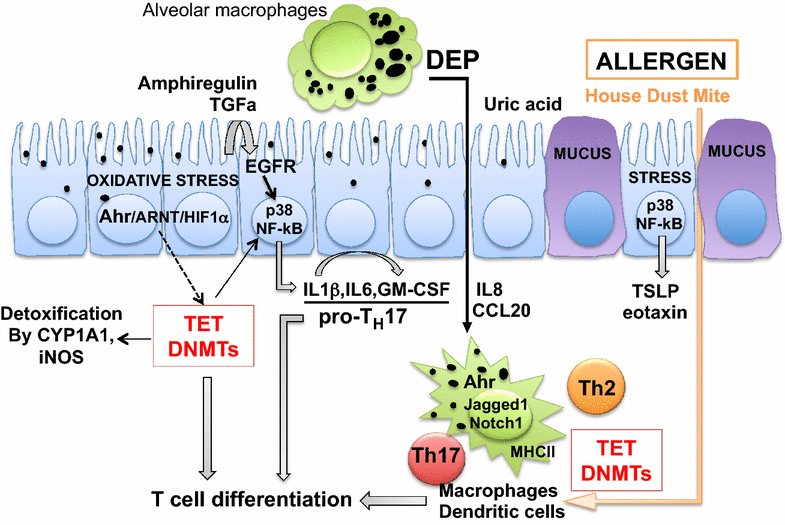
Exposure to traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) has been implicated in asthma development, persistence, and exacerbation. This exposure is highly significant as large segments of the global population resides in zones that are most impacted by TRAP and schools are often located in high TRAP exposure areas. Recent findings shed new light on the epigenetic mechanisms by which exposure to traffic pollution may contribute to the development and persistence of asthma. In order to delineate TRAP induced effects on the epigenome, utilization of newly available innovative methods to assess and quantify traffic pollution will be needed to accurately quantify exposure. This review will summarize the most recent findings in each of these areas. Although there is considerable evidence that TRAP plays a role in asthma, heterogeneity in both the definitions of TRAP exposure and asthma outcomes has led to confusion in the field. Novel information regarding molecular characterization of asthma phenotypes, TRAP exposure assessment methods, and epigenetics are revolutionizing the field. Application of these new findings will accelerate the field and the development of new strategies for interventions to combat TRAP-induced asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; Epigenetics; Traffic pollution.
Figures
References
-
- HEI Panel on the Health Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution . Traffic-related air pollution: a critical review of the literature on emissions, exposure, and health effects. Boston: Health Effects Institute; 2010.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

