Process design of SSCF for ethanol production from steam-pretreated, acetic-acid-impregnated wheat straw
- PMID: 27777624
- PMCID: PMC5070003
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-016-0635-6
Process design of SSCF for ethanol production from steam-pretreated, acetic-acid-impregnated wheat straw
Abstract
Background: Pretreatment is an important step in the production of ethanol from lignocellulosic material. Using acetic acid together with steam pretreatment allows the positive effects of an acid catalyst to be retained, while avoiding the negative environmental effects associated with sulphuric acid. Acetic acid is also formed during the pretreatment and hydrolysis of hemicellulose, and is a known inhibitor that may impair fermentation at high concentrations. The purpose of this study was to improve ethanol production from glucose and xylose in steam-pretreated, acetic-acid-impregnated wheat straw by process design of simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (SSCF), using a genetically modified pentose fermenting yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
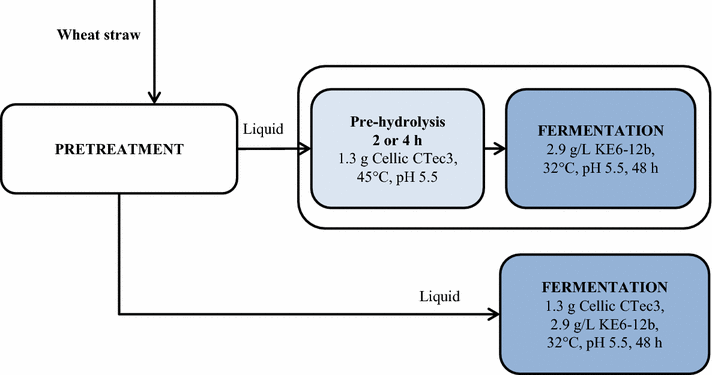
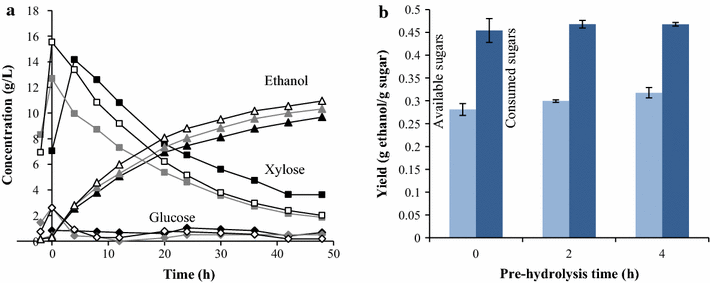
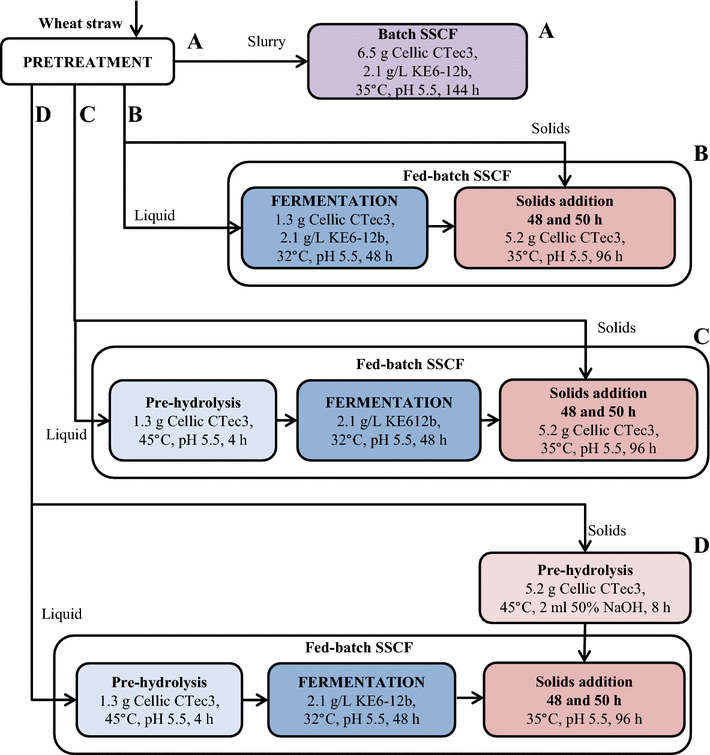
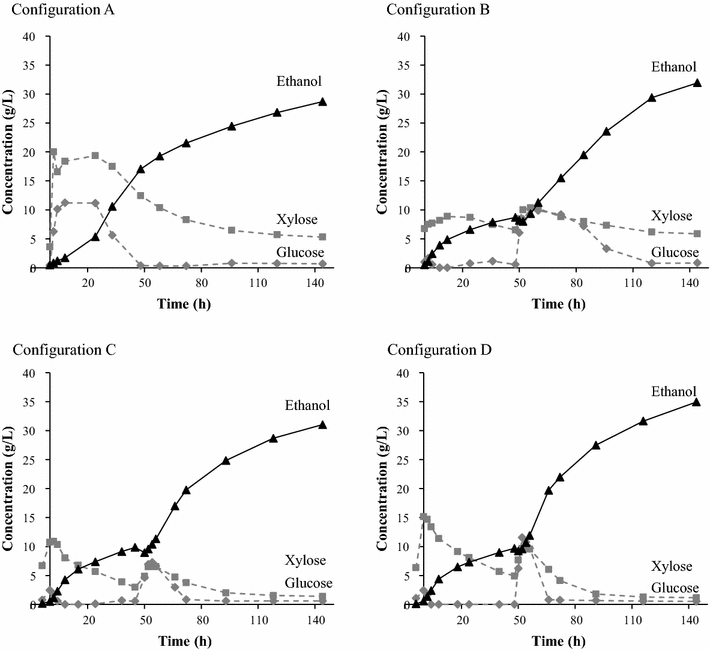
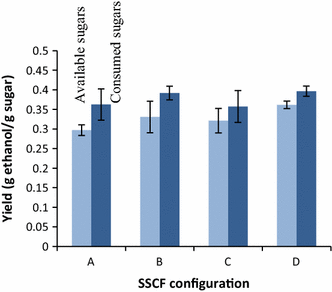
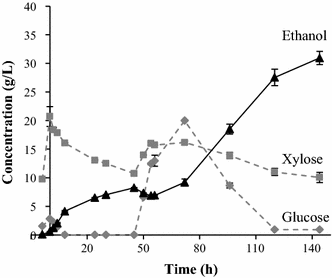
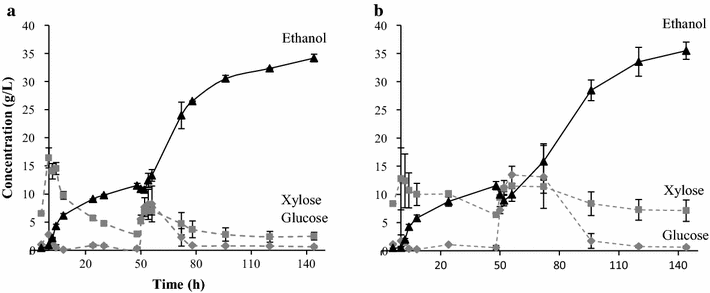
Results: Ethanol was produced from glucose and xylose using both the liquid fraction and the whole slurry from pretreated materials. The highest ethanol concentration achieved was 37.5 g/L, corresponding to an overall ethanol yield of 0.32 g/g based on the glucose and xylose available in the pretreated material. To obtain this concentration, a slurry with a water-insoluble solids (WIS) content of 11.7 % was used, using a fed-batch SSCF strategy. A higher overall ethanol yield (0.36 g/g) was obtained at 10 % WIS.
Conclusions: Ethanol production from steam-pretreated, acetic-acid-impregnated wheat straw through SSCF with a pentose fermenting S. cerevisiae strain was successfully demonstrated. However, the ethanol concentration was too low and the residence time too long to be suitable for large-scale applications. It is hoped that further process design focusing on the enzymatic conversion of cellulose to glucose will allow the combination of acetic acid pretreatment and co-fermentation of glucose and xylose.
Keywords: Acetic acid; Ethanol; Fed-batch; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (SSCF); Steam pretreatment; Wheat straw; Xylose fermentation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Steam pretreatment and fermentation of the straw material "Paja Brava" using simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation.J Biosci Bioeng. 2011 Feb;111(2):167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.10.009. Epub 2010 Nov 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21081285
-
Improving simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of pretreated wheat straw using both enzyme and substrate feeding.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2010 Aug 2;3:17. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-3-17. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2010. PMID: 20678195 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for bioethanol production using corncobs at lab, PDU and demo scales.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013 Jan 14;6(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-2. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013. PMID: 23311728 Free PMC article.
-
Fed-batch SSCF using steam-exploded wheat straw at high dry matter consistencies and a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain: effect of laccase supplementation.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013 Nov 13;6(1):160. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-160. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013. PMID: 24219973 Free PMC article.
-
SSF of steam-pretreated wheat straw with the addition of saccharified or fermented wheat meal in integrated bioethanol production.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013 Nov 29;6(1):169. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-169. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013. PMID: 24286350 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Methane production from wheat straw pretreated with CaO2/cellulase.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 8;11(33):20541-20549. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02437j. eCollection 2021 Jun 3. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479902 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced use of phosphorus and water in sequential dark fermentation and anaerobic digestion of wheat straw and the application of ensiled steam-pretreated lucerne as a macronutrient provider in anaerobic digestion.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Oct 11;11:281. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1280-z. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 30337960 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment for biorefineries: a review of common methods for efficient utilisation of lignocellulosic materials.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019 Dec 23;12:294. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1634-1. eCollection 2019. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2019. PMID: 31890022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioethanol Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass-Challenges and Solutions.Molecules. 2022 Dec 9;27(24):8717. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248717. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity and Abundance of Microbial Communities in UASB Reactors during Methane Production from Hydrolyzed Wheat Straw and Lucerne.Microorganisms. 2020 Sep 11;8(9):1394. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091394. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32932830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Homepage of Beta Renewable’s commercial plant. http://www.betarenewables.com/crescentino/project. Accessed 1 Apr 2016.
-
- Homepage of Poet-DSM’s Project Liberty commercial cellulosic ethanol plant. http://www.poetdsm.com/liberty. Accessed 1 Apr 2016.
-
- Homepage of Abengoa’s commercial plant. http://www.abengoabioenergy.com/web/en/2g_hugoton_project/. Accessed 1 Apr 2016.
-
- Galbe M, Zacchi G. Pretreatment: the key to efficient utilization of lignocellulosic materials. Biomass Bioenergy. 2012;46:70–78. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.03.026. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

