Effects of early-life exposure to THIP on phenotype development in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
- PMID: 27777634
- PMCID: PMC5069883
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-016-9169-2
Effects of early-life exposure to THIP on phenotype development in a mouse model of Rett syndrome
Abstract
Background: Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder caused mostly by disruptions in the MECP2 gene. MECP2-null mice show imbalances in neuronal excitability and synaptic communications. Several previous studies indicate that augmenting synaptic GABA receptors (GABAARs) can alleviate RTT-like symptoms in mice. In addition to the synaptic GABAARs, there is a group of GABAARs found outside the synaptic cleft with the capability to produce sustained inhibition, which may be potential therapeutic targets for the control of neuronal excitability in RTT.
Methods: Wild-type and MECP2-null mice were randomly divided into four groups, receiving the extrasynaptic GABAAR agonist 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol hydrochloride (THIP) and vehicle control, respectively. Low-dose THIP was administered to neonatal mice through lactation. RTT-like symptoms including lifespan, breathing, motor function, and social behaviors were studied when mice became mature. Changes in neuronal excitability and norepinephrine biosynthesis enzyme expression were studied in electrophysiology and molecular biology.
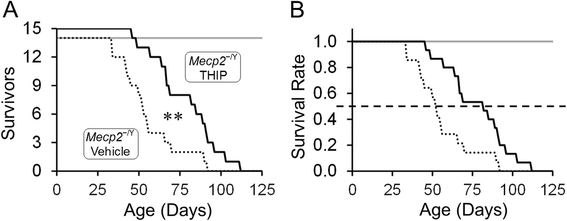
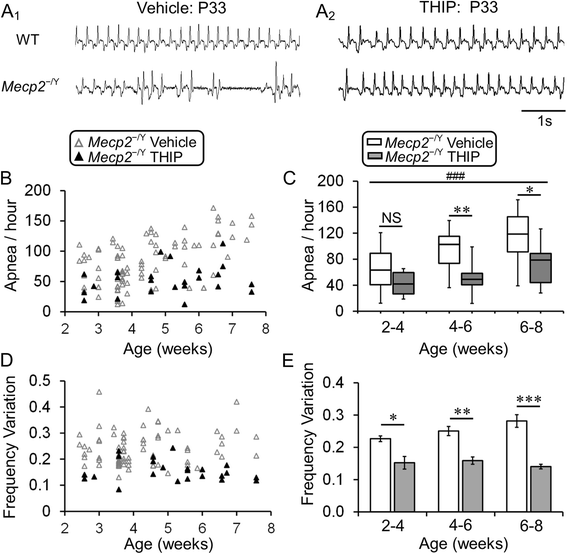
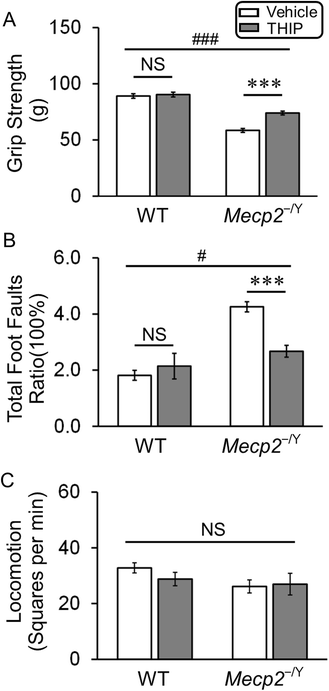
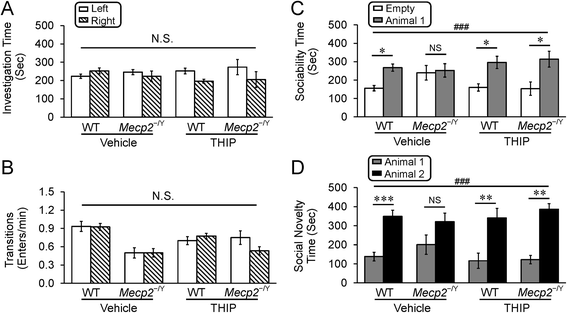
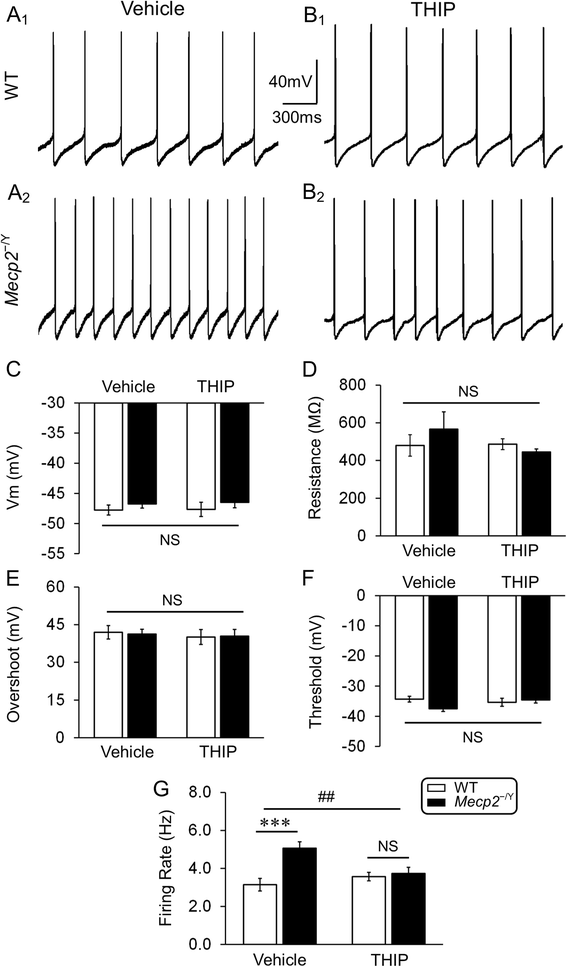
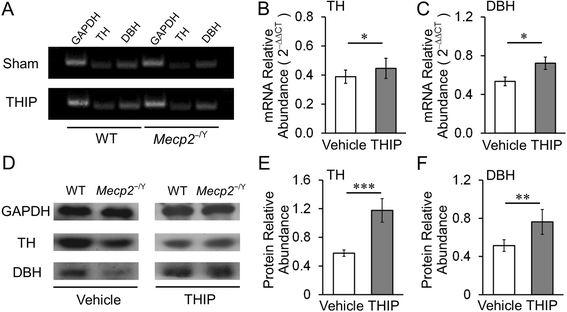
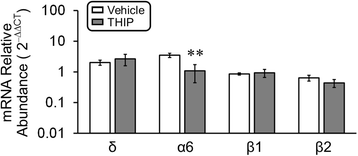
Results: With no evident sedation and other adverse side effects, early-life exposure to THIP extended the lifespan, alleviated breathing abnormalities, enhanced motor function, and improved social behaviors of MECP2-null mice. Such beneficial effects were associated with stabilization of locus coeruleus neuronal excitability and improvement of norepinephrine biosynthesis enzyme expression.
Conclusions: THIP treatment in early lives might be a therapeutic approach to RTT-like symptoms in MECP2-null mice and perhaps in people with RTT as well.
Keywords: Behavior; Gaboxadol; Locus coeruleus; MECP2; Rett syndrome; THIP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of early-life exposure to THIP on brainstem neuronal excitability in the Mecp2-null mouse model of Rett syndrome before and after drug withdrawal.Physiol Rep. 2017 Jan;5(2):e13110. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13110. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28108647 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl CpG Binding Protein 2 Gene Disruption Augments Tonic Currents of γ-Aminobutyric Acid Receptors in Locus Coeruleus Neurons: IMPACT ON NEURONAL EXCITABILITY AND BREATHING.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 24;290(30):18400-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.650465. Epub 2015 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25979331 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chronic exposure to low dose THIP on brainstem neuronal excitability in mouse models of Rett syndrome: Evidence from symptomatic females.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Apr;116:288-299. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28069353
-
Exploring the possible link between MeCP2 and oxidative stress in Rett syndrome.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt A):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 May 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25960047 Review.
-
MeCP2 expression and function during brain development: implications for Rett syndrome's pathogenesis and clinical evolution.Brain Dev. 2005 Nov;27 Suppl 1:S77-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2004.10.008. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Brain Dev. 2005. PMID: 16182491 Review.
Cited by
-
Treating Rett syndrome: from mouse models to human therapies.Mamm Genome. 2019 Jun;30(5-6):90-110. doi: 10.1007/s00335-019-09793-5. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Mamm Genome. 2019. PMID: 30820643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective GABAergic neurotransmission in the nucleus tractus solitarius in Mecp2-null mice, a model of Rett syndrome.Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Jan;109(Pt A):25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.09.006. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Neurobiol Dis. 2018. PMID: 28927958 Free PMC article.
-
Early Postnatal Treatment with Valproate Induces Gad1 Promoter Remodeling in the Brain and Reduces Apnea Episodes in Mecp2-Null Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 18;20(20):5177. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205177. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31635390 Free PMC article.
-
Excitation and Inhibition Imbalance in Rett Syndrome.Front Neurosci. 2022 Feb 18;16:825063. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.825063. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35250460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antitussive cloperastine improves breathing abnormalities in a Rett Syndrome mouse model by blocking presynaptic GIRK channels and enhancing GABA release.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 1;176:108214. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108214. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32622786 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

