Integrating DNA methylation and microRNA biomarkers in sputum for lung cancer detection
- PMID: 27777637
- PMCID: PMC5070138
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0275-5
Integrating DNA methylation and microRNA biomarkers in sputum for lung cancer detection
Abstract
Background: Abnormal microRNA (miRNA) expressions and promoter methylation of genes detected in sputum may provide biomarkers for non-small lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, we evaluate the individual and combined analysis of the two classes of sputum molecular biomarkers for NSCLC detection.
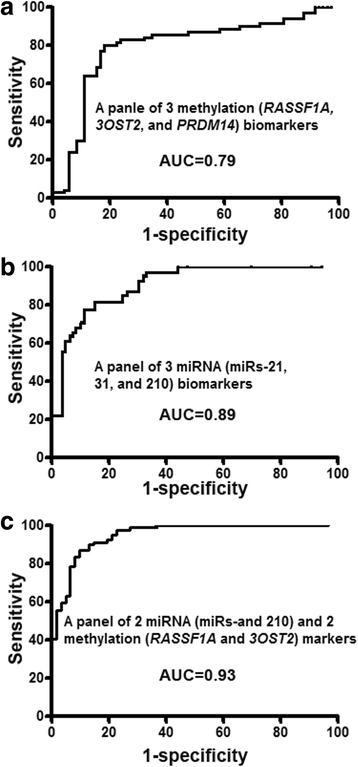
Results: We analyze expression of 3 miRNAs (miR-21, miR-31, and miR-210) and methylation of 3 genes (RASSF1A, PRDM14, and 3OST2), which were previously identified as potential biomarkers for NSCLC, in sputum of a set of 117 stage I NSCLC patients and 174 cancer-free smokers. The results are validated in a different set of 144 stage I NSCLC patients and 171 controls. The panel of 3 miRNA biomarkers has 81.5 % sensitivity and 85.9 % specificity; the panel of 3 methylation biomarkers displays 82.9 % sensitivity and 76.4 % specificity for NSCLC detection. Integrated analysis of 2 miRNAs (miR-31 and miR-210) and 2 genes (RASSF1A and 3OST2) yields higher sensitivity (87.3 %) and specificity (90.3 %) compared with the individual panels of the biomarkers (P < 0.05). Combined analysis of all the 3 miRNAs and 3 genes does not have performance superior to that of the panel of 2 miRNAs and 2 genes (P > 0.05). The performance of combined use of the two classes of biomarkers was confirmed in the validation set.
Conclusions: The integration of two different classes of biomarkers synergistically improves both the sensitivity and the specificity for the early detection of NSCLC.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Diagnosis; Lung cancer; MicroRNA; Sputum.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Thorac Cancer. 2020 Mar;11(3):762-768. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13337. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31994346 Free PMC article.
-
Sputum microRNA profiling: a novel approach for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Invest Med. 2012 Oct 6;35(5):E271. doi: 10.25011/cim.v35i5.18700. Clin Invest Med. 2012. PMID: 23043708 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential circulating miRNA signature for early detection of NSCLC.Cancer Genet. 2017 Oct;216-217:150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Cancer Genet. 2017. PMID: 29025589
-
microRNA and Lung Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;889:153-77. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-23730-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26659001 Review.
-
The Indirect Efficacy Comparison of DNA Methylation in Sputum for Early Screening and Auxiliary Detection of Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Jun 23;14(7):679. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14070679. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28644424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methylated Cell-Free Tumor DNA in Sputum as a Tool for Diagnosing Lung Cancer-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 24;16(3):506. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030506. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of early lung cancer among military personnel (DECAMP) consortium: study protocols.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Mar 7;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0825-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 30845938 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of microRNAs in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms, Diagnostics and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 15;26(8):3736. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083736. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An epigenetic classifier for early stage lung cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 May 22;10:68. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0502-3. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29796119 Free PMC article.
-
Panomics for Precision Medicine.Trends Mol Med. 2018 Jan;24(1):85-101. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Trends Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29217119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cancer facts & figures 2012. American Cancer Society (ACS). Journal of Consumer Health on the Internet. 2012; 16:366–367.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

