Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer
- PMID: 27777769
- PMCID: PMC5067916
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-016-0165-6
Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer
Abstract
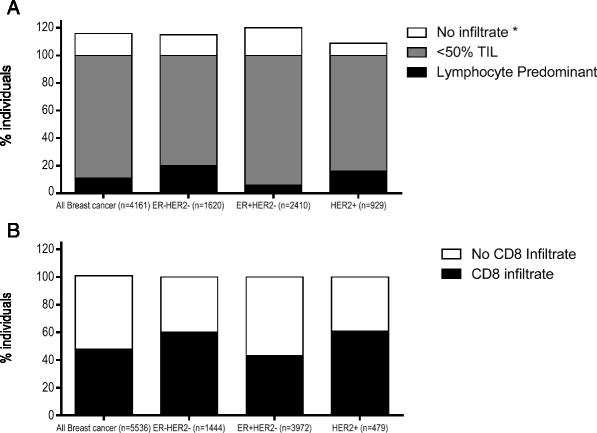
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) play an essential role in mediating response to chemotherapy and improving clinical outcomes in all subtypes of breast cancer. Triple negative breast cancers (TN) are most likely to have tumors with >50 % lymphocytic infiltrate, termed lymphocyte predominant breast cancer, and derive the greatest survival benefit from each 10 % increase in TIL. The majority of HER2+ breast cancers have similar level of immune infiltrate as TN breast cancer yet the presence of TILs has not shown the same survival benefit. For HER2+ breast cancers, type 1 T-cells, either increased TBET+ tumor infiltration or increased type 1 HER2-specific CD4+ T-cells in the peripheral blood, are associated with better outcomes. Hormone receptor positive HER2 negative tumors tend to have the least immune infiltrate yet are the only breast cancer subtype to show worse prognosis with increased FOXP3 regulatory T-cell infiltrate. Notably, all breast cancer subtypes have tumors with low, intermediate, or high TIL infiltrate. Tumors with high TILs may also have increased PD-L1 expression which might be the reason that TN breast cancer seems to demonstrate the most robust clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy but further investigation is needed. Tumors with intermediate or low levels of pre-treatment immune infiltrate, on the other hand, may benefit from an intervention that may increase TIL, particularly type 1 T-cells. Examples of these interventions include specific types of cytotoxic chemotherapy, radiation, or vaccine therapy. Therefore, the systematic evaluation of TIL and specific populations of TIL may be able to both guide prognosis and the appropriate sequencing of therapies in breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CD8 T-cell; FOXP3; Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, Van Eenoo F, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(7):860–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0902. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
