Antitumor activity of nivolumab on hemodialysis after renal allograft rejection
- PMID: 27777773
- PMCID: PMC5067882
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-016-0171-8
Antitumor activity of nivolumab on hemodialysis after renal allograft rejection
Abstract
Background: Nivolumab (Opdivo™) is a novel IgG4 subclass programmed death-1 (PD-1) inhibiting antibody that has demonstrated breakthrough-designation anti-tumor activity. To date, clinical trials of nivolumab and other checkpoint inhibitors have generally excluded patients with solid organ transplantation and patients with concurrent immunosuppression. However, organ transplant recipients are at high-risk of development of malignancy as a result of suppressed immune surveillance of cancer.
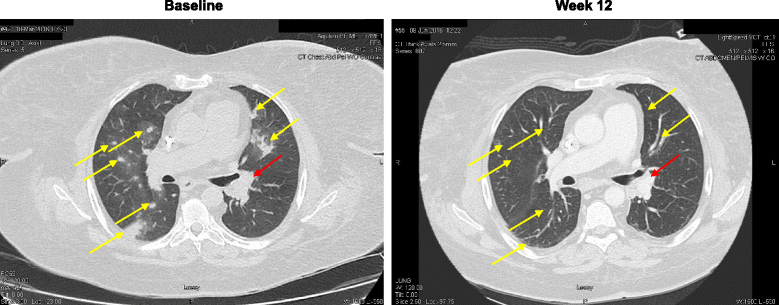
Case presentation: We illustrate the outcomes of a 63 year-old type I diabetic female patient who developed pulmonary metastatic, BRAF wild-type cutaneous melanoma 10 years after renal transplantation. After downward titration of the patient's immunosuppressive medications and extensive multidisciplinary review, she was treated with nivolumab in the first-line setting. Within 1 week of administration, the patient experienced acute renal allograft rejection, renal failure and concurrent diabetic ketoacidosis due to steroid therapy. Allograft function did not return, but patient made a full clinical recovery after being placed on hemodialysis. Subsequently, the patient had clinical disease progression off therapy and required re-challenge with nivolumab on hemodialysis, resulting in ongoing clinical and radiographic response.
Conclusions: This case illustrates multiple practical challenges and dangers of administering anti-PD1 immune checkpoint inhibitors to patients with solid-organ transplantation including need for titration of immunosuppressive medications, risks of allograft rejection, and treatment during hemodialysis.
Keywords: Acute allograft rejection; Anti-PD-1 therapy; Hemodialysis; Melanoma; Nivolumab; Organ transplant.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Donor-derived cell-free DNA detects kidney transplant rejection during nivolumab treatment.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Jul 12;7(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0653-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31300068 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoint inhibitors in chronic kidney failure and an organ transplant recipient.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Nov;67:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.07.026. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27614165
-
PD 1 checkpoint inhibition in solid organ transplants: 2 sides of a coin - case report.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Aug 20;19(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-1003-5. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30126374 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Organ Transplant Patients.J Immunother. 2017 Sep;40(7):277-281. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000180. J Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28719552 Review.
-
Programmed Cell Death 1 (PD-1) Inhibitors in Renal Transplant Patients with Advanced Cancer: A Double-Edged Sword?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 3;20(9):2194. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092194. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31058839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors for solid organ transplant recipients: clinical updates.Korean J Transplant. 2022 Jun 30;36(2):82-98. doi: 10.4285/kjt.22.0013. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Korean J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35919193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Checkpoint Inhibitors.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Feb 22;116(8):119-126. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0119. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019. PMID: 30940340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features, predictive correlates, and pathophysiology of immune-related adverse events in immune checkpoint inhibitor treatments in cancer: a short review.Immunotargets Ther. 2017 Oct 10;6:73-82. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S126227. eCollection 2017. Immunotargets Ther. 2017. PMID: 29067284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in End Stage Kidney Disease Patients, Single Center Experience and Review of the Literature.Kidney360. 2020 Mar 18;1(5):399-402. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000422020. eCollection 2020 May 28. Kidney360. 2020. PMID: 35369378 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Donor-derived cell-free DNA detects kidney transplant rejection during nivolumab treatment.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Jul 12;7(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0653-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31300068 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials