High-dose interleukin2 - a 10-year single-site experience in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: careful selection of patients gives an excellent outcome
- PMID: 27777776
- PMCID: PMC5067981
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-016-0174-5
High-dose interleukin2 - a 10-year single-site experience in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: careful selection of patients gives an excellent outcome
Abstract
Background: VEGF-targeted therapy has become the mainstay of treatment for majority of mRCC patients. For most patients, benefit is short-lived and therefore treatment remains palliative in intent. HD IL2 is an effective immunotherapy treatment capable of durable remission in some patients but its unselected use has been difficult due to its modest response rate and considerable adverse effects. Using set pathology criteria as a selection tool in clinical practice, we have been able to show improved outcomes in our previous report. Here, we present an updated and extended report of this treatment and seek to explore any pathological, clinical and treatment variables likely to predict better outcomes.
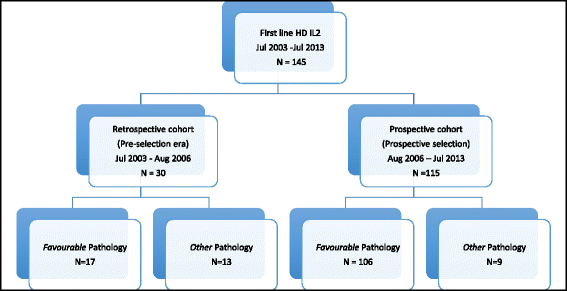
Methods: This is an extension of a previously reported clinical audit, which includes mRCC cases treated with HD IL2 between 2003 and 2013. Since 2006, tumour specimens of potential candidates were routinely reviewed prospectively and stratified into Favourable or Other categories based on constitution of histological growth pattern, namely alveolar or solid versus papillary and/or sarcomatoid architecture; clear cell versus granular cell cytoplasmic morphology. HD IL2 was preferentially offered to patients with Favourable pathology. Outcome evaluation includes response rates, survival, and treatment tolerance. Multivariate analysis was performed to explore potential prognostic and predictive factors.
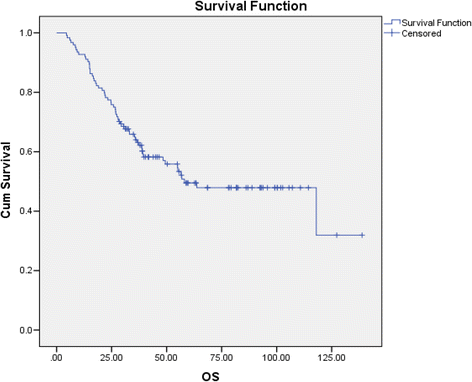
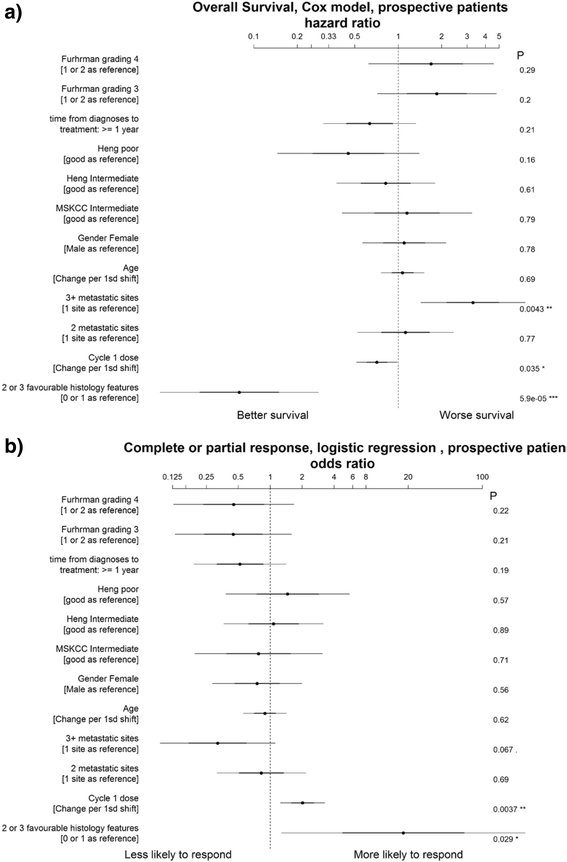
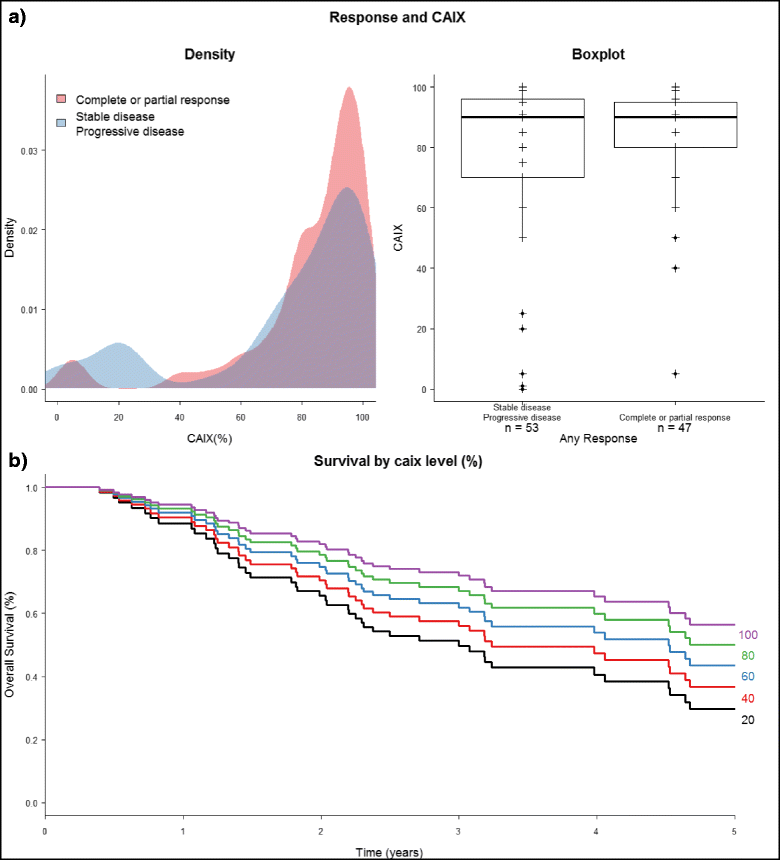
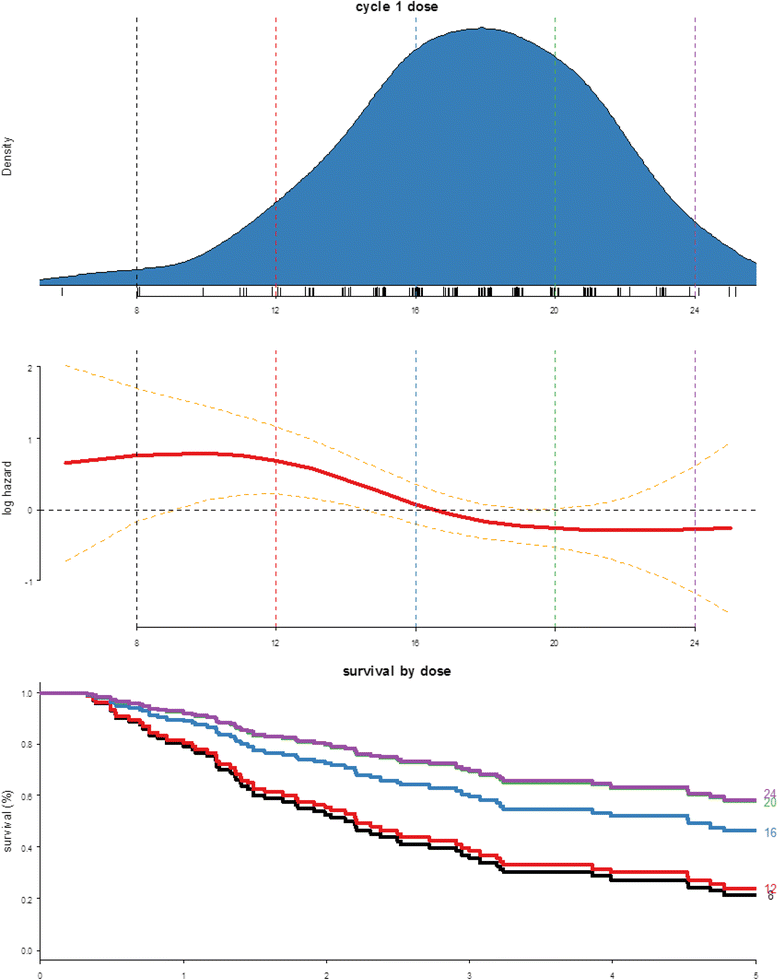
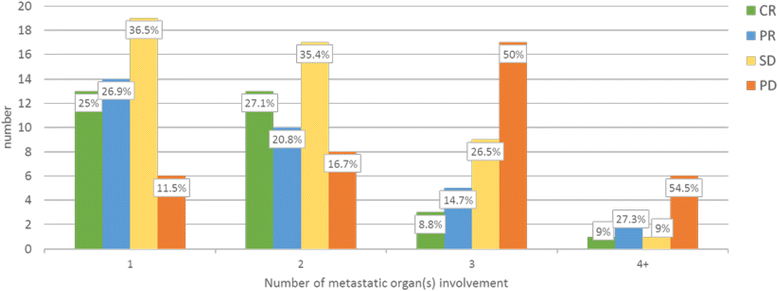
Results: Among prospectively selected patients with Favourable pathology (n = 106), overall response rate was 48.1 % (51/106) with CR rate of 21.6 % (23/106). Median OS was 58.1 months. Factors associated with significantly better response and/or survival includes favourable pathology pattern, higher cycle 1 tolerance and lower number of metastatic organ sites (<3). CAIX (Carbonic anhydrase 9) has prognostic value but is not predictive of response. Toxicities were those expected of IL2 but were manageable on general medical wards, with no treatment-related death. Importantly most complete responses were durable with 76 % (23/30) cases remained relapse-free (median 39 months follow up) and 2 of the seven who relapsed had had long-term disease free survival after resection of oligometastatic relapse.
Conclusions: Our experience shows that HD IL2 remains an effective and safe treatment in well-selected cases of mRCC. The result in this single-institution patient series confirms similar outcomes to our previously reported retrospective series. Given the prospect of long-term remission, fit patients with Favourable histology and low disease burden should be considered for HD IL2 in an experienced centre. Better understanding has been gained from this in-depth analysis especially the examination of possible response predictors and strategies that can improve treatment outcome.
Keywords: Cytokine therapy; High dose interleukin2; Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; Pathology selection criteria.
Figures
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J, Nathan P, Staehler M, de Souza P, Merchan JR, Boleti E, Fife K, Jin J, Jones R, Uemura H, De Giorgi U, Harmenberg U, Wang J, Sternberg CN, Deen K, McCann L, Hackshaw MD, Crescenzo R, Pandite LN, Choueiri TK. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):722–731. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1303989. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J, Nathan P, Staehler M, De Souza P, Merchan JR, Fife K, Jin J, Jones R, Uemura H, De Giorgi U, Harmenberg U, Wang J, Cella D, McCann L, Deen K, Choueri TK. ESMO. 2012. Randomized, open label, phase III trial of pazopanib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC); results of the COMPARZ trial; p. LBA8.
-
- Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA, Kavina A, Zarbá JJ, Chen M, McCann L, Pandite L, Roychowdhury DF, Hawkins RE. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1061–1068. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.9764. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
