Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in HBeAg-positive patients in China: a health economic analysis
- PMID: 27777855
- PMCID: PMC5052247
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-3404-x
Telbivudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in HBeAg-positive patients in China: a health economic analysis
Abstract
Background: Nucleos(t)ide analogs (NUCs) are the standard of care for chronic hepatitis B (CHB). The present analysis aimed to determine the cost effectiveness of NUCs in Chinese healthcare settings.
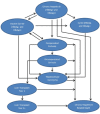
Methods: A Markov model was used to simulate two therapeutic strategies for a hypothetical patient cohort diagnosed with hepatitis B e antigen-positive CHB, unwilling or unable to receive interferon therapy, and about to start treatment with any NUC. The first strategy included NUC monotherapy without sequencing (telbivudine [LDT], entecavir [ETV], tenofovir [TDF], lamivudine [LAM], adefovir dipivoxil [ADV], and combination therapies of either LDT and ADV or LDT and TDF, followed by best supportive care [BSC]). The second strategy included sequential therapies of individual NUCs: LAM → ADV, ADV → LAM, LDT → ADV, and ETV → ADV, followed by BSC. The analysis included two scenarios: with and without costs due to nephrotoxicity. Renal impact was quantified as costs alone, without consideration for quality of life decrements.
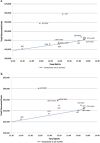
Results: When renal impact was not considered, without treatment sequencing, LDT was cost effective compared with other NUCs. Amongst the strategies with sequencing, LDT → ADV was cost effective. The results were similar when renal impact was considered. However, LDT strategy demonstrated better cost effectiveness. In probabilistic sensitivity analysis, in both scenarios, LDT → ADV sequence was cost effective with 51 % probability even at willingness to pay of $20,000.
Conclusion: Use of LDT, as compared with other NUCs, is cost effective in CHB treatment in Chinese healthcare settings. Considering the detrimental renal impact, overall costs for all treatment options were increased. However, the increase for LDT was comparatively small.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; Cost effectiveness; Renal impairment; Telbivudine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness analysis of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for treatment of chronic hepatitis B in China.Hepatol Int. 2016 Nov;10(6):924-936. doi: 10.1007/s12072-016-9741-6. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Hepatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27271357
-
Efficacy and safety of three adefovir-based combination therapies in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with suboptimal response to adefovir monotherapy.J Viral Hepat. 2017 Nov;24 Suppl 1:21-28. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12792. J Viral Hepat. 2017. PMID: 29082645
-
Efficacy and safety of telbivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy and entecavir monotherapy for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with resistance to adefovir dipivoxil.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Apr;20 Suppl 1:40-5. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12062. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23458523 Clinical Trial.
-
[Compare the effect of combined therapy between telbivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil and lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil corresponding to renal function in patients with hepatitis B virus infection].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 20;26(4):288-293. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.011. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29996341 Chinese.
-
Entecavir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection.Health Technol Assess. 2009 Oct;13 Suppl 3:31-6. doi: 10.3310/hta13suppl3/05. Health Technol Assess. 2009. PMID: 19846026 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-vaccination anti-HBs testing among healthcare workers: More economical than post-exposure management for Hepatitis B.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2020 Jun 19;28:e3278. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.3534.3278. eCollection 2020. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2020. PMID: 32578749 Free PMC article.
-
Are Published Health Economic Models for Chronic Hepatitis B Appropriately Capturing the Benefits of HBsAg Loss? A Systematic Literature Review.Pharmacoecon Open. 2020 Sep;4(3):403-418. doi: 10.1007/s41669-019-00175-w. Pharmacoecon Open. 2020. PMID: 31428938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kushenin combined with adefovir dipivoxil affects the HBV-DNA load in serum, immune functions and liver functions of patients with chronic hepatitis B.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):5837-5842. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5266. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29285129 Free PMC article.
-
Baseline serum miR-125b levels predict virologic response to nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Nov;16(5):3805-3812. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6685. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30344656 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

