The critical care response to a hospital outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: an observational study
- PMID: 27778310
- PMCID: PMC5078123
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-016-0203-z
The critical care response to a hospital outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) has caused several hospital outbreaks, including a major outbreak at King Abdulaziz Medical City, a 940-bed tertiary-care hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (August-September 2015). To learn from our experience, we described the critical care response to the outbreak.
Methods: This observational study was conducted at the Intensive Care Department which covered 5 ICUs with 60 single-bedded rooms. We described qualitatively and, as applicable, quantitatively the response of intensive care services to the outbreak. The clinical course and outcomes of healthcare workers (HCWs) who had MERS were noted.
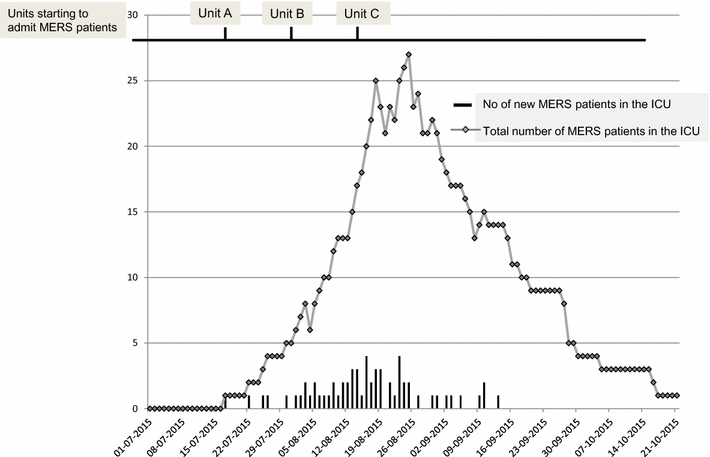
Results: Sixty-three MERS patients were admitted to 3 MERS-designated ICUs during the outbreak (peak census = 27 patients on August 25, 2015, and the last new case on September 13, 2015). Most patients had multiorgan failure. Eight HCWs had MERS requiring ICU admission (median stay = 28 days): Seven developed acute respiratory distress syndrome, four were treated with prone positioning, four needed continuous renal replacement therapy and one had extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. The hospital mortality of ICU MERS patients was 63.4 % (0 % for the HCWs). In response to the outbreak, the number of negative-pressure rooms was increased from 14 to 38 rooms in 3 MERS-designated ICUs. Patients were managed with a nurse-to-patient ratio of 1:0.8. Infection prevention practices were intensified. As a surrogate, surface disinfectant and hand hygiene gel consumption increased by ~30 % and 17 N95 masks were used per patient/day on average. Family visits were restricted to 2 h/day. Although most ICU staff expressed concerns about acquiring MERS, all reported to work normally. During the outbreak, 27.0 % of nurses and 18.4 % of physicians working in the MERS-designated ICUs reported upper respiratory symptoms, and were tested for MERS-CoV. Only 2/196 (1.0 %) ICU nurses and 1/80 (1.3 %) physician tested positive, had mild disease and recovered fully. The total sick leave duration was 138 days for nurses and 30 days for physicians.
Conclusions: Our hospital outbreak of MERS resulted in 63 patients requiring organ support and prolonged ICU stay with a high mortality rate. The ICU response required careful facility and staff management and proper infection control and prevention practices.
Keywords: Critical care; Disaster planning; Disease outbreak; Middle East respiratory syndrome; Saudi Arabia; Severe acute respiratory infection.
Figures
References
-
- Saad M, Omrani AS, Baig K, Bahloul A, Elzein F, Matin MA, et al. Clinical aspects and outcomes of 70 patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a single-center experience in Saudi Arabia. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;29:301–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.09.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The World Health Organization. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/. Accessed 27 Sept 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials