Hearing Changes After Intratympanically Applied Steroids for Primary Therapy of Sudden Hearing Loss: A Meta-analysis Using Mathematical Simulations of Drug Delivery Protocols
- PMID: 27779563
- PMCID: PMC5154844
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001254
Hearing Changes After Intratympanically Applied Steroids for Primary Therapy of Sudden Hearing Loss: A Meta-analysis Using Mathematical Simulations of Drug Delivery Protocols
Abstract
Objective: Controlled and uncontrolled studies with primary intratympanic or combined intratympanic and systemic application of glucocorticosteroids for idiopathic sudden hearing loss were analyzed by means of a meta-analysis in an attempt to establish optimal local drug delivery protocols.
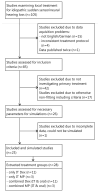
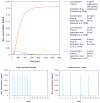
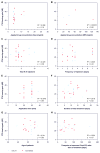
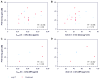
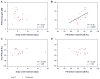
Study design: A total of 25 studies with 28 treatment groups between January 2000 and June 2014 were selected that adequately described drug delivery protocols. Cochlear drug levels were calculated by a validated computer model of drug dispersion in the inner ear fluids based on the concentration and volume of glucocorticoids applied, the time the drug remained in the middle ear, and the specific timing of injections. Various factors were compared with hearing outcome, including baseline data, individual parameters of the application protocols, calculated peak concentration (Cmax), and total dose (area under the curve).
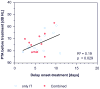
Results: There was no dependence of hearing outcome on individual parameters of the application protocol, Cmax, or area under the curve. Final hearing threshold was notably independent of delay of treatment.
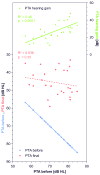
Conclusion: During primary intratympanic or combined steroid therapy of idiopathic sudden hearing loss, the tendency toward early treatment having a positive effect on hearing improvement is thought to be a "sham effect," likely related to spontaneous recovery. Change in pure-tone average may not be an adequate outcome parameter to assess effectiveness of the intervention, as it depends on the degree of initial hearing loss. Final pure-tone average provides a better alternative.
Figures
References
-
- Vlastarakos PV, Papacharalampous G, Maragoudakis P, et al. Are intra-tympanically administered steroids effective in patients with sudden deafness? Implications for current clinical practice. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;269:363–80. - PubMed
-
- Lavigne P, Lavigne F, Saliba I. Intratympanic corticosteroids injections: a systematic review of literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Huon LK, Fang TY, Wang PC. Outcomes of intratympanic gentamicin injection to treat Meniere's disease. Otol Neurotol. 2012;33:706–14. - PubMed
-
- Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146:S1–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

