Effects of an Offshore Wind Farm (OWF) on the Common Shore Crab Carcinus maenas: Tagging Pilot Experiments in the Lillgrund Offshore Wind Farm (Sweden)
- PMID: 27780212
- PMCID: PMC5079560
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165096
Effects of an Offshore Wind Farm (OWF) on the Common Shore Crab Carcinus maenas: Tagging Pilot Experiments in the Lillgrund Offshore Wind Farm (Sweden)
Abstract
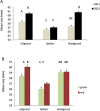
Worldwide growth of offshore renewable energy production will provide marine organisms with new hard substrate for colonization in terms of artificial reefs. The artificial reef effect is important when planning offshore installations since it can create habitat enhancement. Wind power is the most advanced technology within offshore renewable energy sources and there is an urgent need to study its impacts on the marine environment. To test the hypothesis that offshore wind power increases the abundance of reef species relative to a reference area, we conduct an experiment on the model species common shore crab (Carcinus maenas).Overall, 3962 crabs were captured, observed, marked and released in 2011 and 1995 crabs in 2012. Additionally, carapace size, sex distribution, color morphs and body condition was recorded from captured crabs. We observed very low recapture rates at all sites during both years which made evaluating differences in population sizes very difficult. However, we were able to estimate population densities from the capture record for all three sites. There was no obvious artificial reef effect in the Lillgrund wind farm, but a spill-over effect to nearby habitats cannot be excluded. We could not find any effect of the wind farm on either, morphs, sex distribution or condition of the common shore crab. Our study found no evidence that Lillgrund wind farm has a negative effect on populations of the common shore crab. This study provides the first quantitative and experimental data on the common shore crab in relation to offshore wind farms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Greening Blue Energy: Identifying and managing the biodiversity risks and opportunities of offshore renewable energy, (2010).
-
- Rodrigues S, Restrepo C, Kontos E, Teixeira Pinto R, Bauer P. Trends of offshore wind projects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2015;49:1114–35.
-
- Inger R, Attrill MJ, Bearhop S, Broderick AC, Grecian WJ, Hodgson DJ, et al. Marine renewable energy: potential benefits to biodiversity? An urgent call for research. Journal of Applied Ecology. 2009. December;46(6):1145–53.
-
- Breitburg DL, Palmer MA, Loher T. Larval Distributions and the Spatial Patterns of Settlement of an Oyster Reef Fish—Responses to Flow and Structure. Marine Ecology-Progress Series. [Article]. 1995. September;125(1–3):45–60.
-
- Snelgrove PVR, Butman CA. ANIMAL SEDIMENT RELATIONSHIPS REVISITED—CAUSE VERSUS EFFECT. In: Ansell AD, Gibson RN, Barnes M, editors. Oceanography and Marine Biology, Vol 32: An Annual Review1994. p. 111–77.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

