T-cell Receptor Signaling Activates an ITK/NF-κB/GATA-3 axis in T-cell Lymphomas Facilitating Resistance to Chemotherapy
- PMID: 27780854
- PMCID: PMC5405012
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1996
T-cell Receptor Signaling Activates an ITK/NF-κB/GATA-3 axis in T-cell Lymphomas Facilitating Resistance to Chemotherapy
Erratum in
-
Correction: T-cell Receptor Signaling Activates an ITK/NF-κB/GATA-3 Axis in T-cell Lymphomas Facilitating Resistance to Chemotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 1;23(19):5995. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2115. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28972087 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: T-cell lymphomas are a molecularly heterogeneous group of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) that account for a disproportionate number of NHL disease-related deaths due to their inherent and acquired resistance to standard multiagent chemotherapy regimens. Despite their molecular heterogeneity and frequent loss of various T cell-specific receptors, the T-cell antigen receptor is retained in the majority of these lymphomas. As T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement activates a number of signaling pathways and transcription factors that regulate T-cell growth and survival, we examined the TCR's role in mediating resistance to chemotherapy.Experimental Design: Genetic and pharmacologic strategies were utilized to determine the contribution of tyrosine kinases and transcription factors activated in conventional T cells following TCR engagement in acquired chemotherapy resistance in primary T-cell lymphoma cells and patient-derived cell lines.Results: Here, we report that TCR signaling activates a signaling axis that includes ITK, NF-κB, and GATA-3 and promotes chemotherapy resistance.Conclusions: These observations have significant therapeutic implications, as pharmacologic inhibition of ITK prevented the activation of this signaling axis and overcame chemotherapy resistance. Clin Cancer Res; 23(10); 2506-15. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
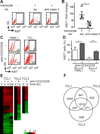

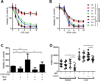

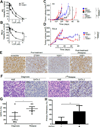
References
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4124–4130. - PubMed
-
- Mak V, Hamm J, Chhanabhai M, Shenkier T, Klasa R, Sehn LH, et al. Survival of patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma after first relapse or progression: spectrum of disease and rare long-term survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:1970–1976. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

