Toll-like receptor agonists partially restore the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I interferon in Sézary syndrome
- PMID: 27780938
- PMCID: PMC5342689
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12816
Toll-like receptor agonists partially restore the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I interferon in Sézary syndrome
Abstract
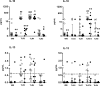
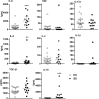
Sézary syndrome (SS) carries a poor prognosis, and infections represent the most frequent cause of death in SS patients. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a family of innate immune receptors that induce protective immune responses against infections. We sought to evaluate the ability of TLR agonists to induce inflammatory cytokine, Th2 cytokine, and type I interferon (IFN-I) production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of untreated SS patients. We detected impaired IL-6, IL-10 and IL-13 secretion by PBMC induced by the agonists for TLR5, TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9 in SS patients, while it was partially recovered by TLR2/TLR4 and TLR7/8 agonists TNF secretion was restored following stimulation with TLR2/TLR4 agonists. IFN-γ was scarcely produced upon TLR activation in SS cells, albeit TLR 7/8 (CL097) enhanced their secretion at lower levels than the control group. TLR9 agonist efficiently induced IFN-I in SS patients, although this positive regulation was not observed for other cytokines, in direct contrast to the broad activity of CL097. Among the TLR agonists, TLR4 was able to induce pro-inflammatory, IL-10 and Th2 secretion, while TLR7-8 agonist induced the inflammatory cytokines, IFN-I and IFN-γ. These findings reveal a dysfunctional cytokine response upon both extracellular and intracellular TLR activation in SS patients, which was partially restored by TLRs agonists.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; Toll-like receptor agonists; cytokines; innate immunity; type I interferon; Sézary syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures


References
-
- Imam MH, Shenoy PJ, Flowers CR, Phillips A, Lechowicz MJ. Incidence and survival patterns of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas in the United States. Leukemia & Lymphoma. 2013;54:752–759. - PubMed
-
- Rook AH, Vowels BR, Jaworsky C, Singh A, Lessin SR. The immunopathogenesis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Abnormal cytokine production by Sezary T cells. Archives of Dermatology. 1993;129:486–489. - PubMed
-
- Rook AH, Heald P. The immunopathogenesis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America. 1995;9:997–1010. - PubMed
-
- Vowels BR, Cassin M, Vonderheid EC, Rook AH. Aberrant cytokine production by Sezary syndrome patients: cytokine secretion pattern resembles murine Th2 cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1992;99:90–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

