The findings of CT and MRI in patients with metanephric adenoma
- PMID: 27784295
- PMCID: PMC5081663
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-016-0535-x
The findings of CT and MRI in patients with metanephric adenoma
Abstract
Background: Metanephric adenoma (MA) is a benign renal tumor that is difficult to distinguish from a malignant tumor via traditional radiography. The diagnosis of MA is often dependent on postsurgical histopathological examination. In the present report, the imaging features of MA on computer tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were retrospectively evaluated.
Methods: Eight MA patients, 17-67 years of age, were pathologically confirmed and recruited between April 2009 and November 2014. Four of the eight patients were female. All patients underwent CT scanning, and one patient underwent MRI scanning. Three patients underwent CTA of the renal arteries. All patients underwent resection surgery (radical nephrectomy in five and nephron-sparing surgery in three patients).
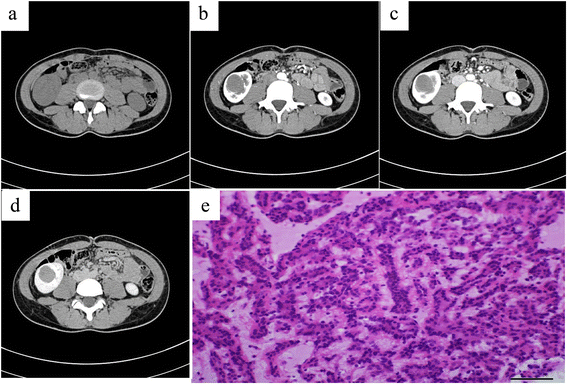
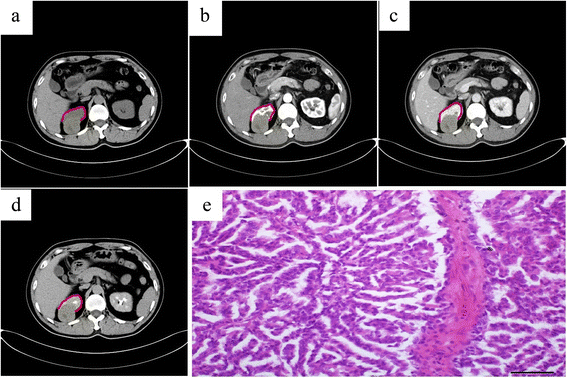
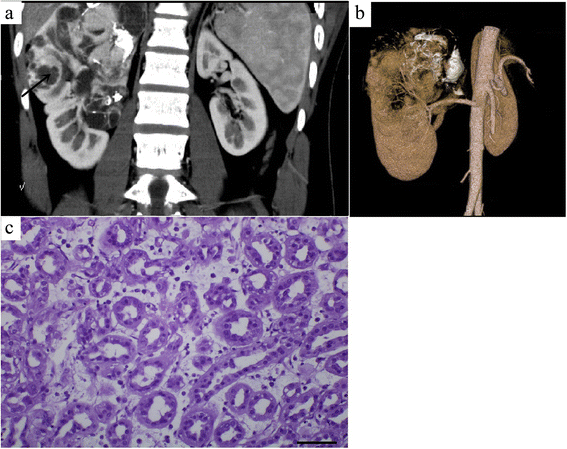
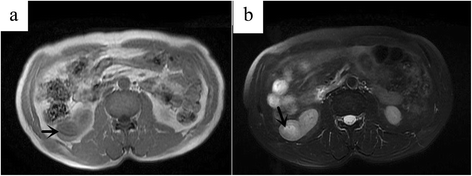
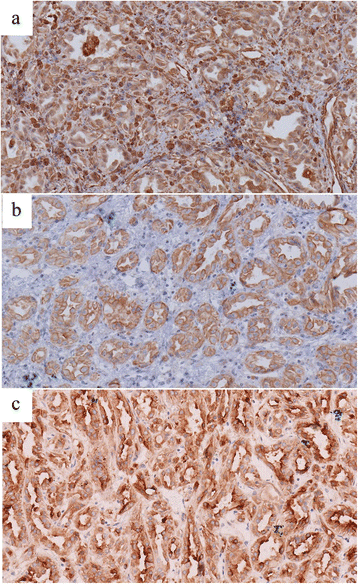
Results: The average tumor size was 44.0 ± 23.6 mm. The lesions in 87.5 % cases were located both in the renal cortex and medulla and exhibited exophytic growth. Plain CT showed that MA tumors were solid, and the average CT value was 37.9 ± 6.7 HU. Dynamic contrast-enhanced CT revealed that enhanced degrees of MA tumors in the renal cortex, renal parenchymal, and pelvic phase were all lower than that of normal renal parenchyma. A slight enhancement in the renal cortex phase and an even higher enhancement in the renal parenchymal phase were observed in seven of the cases. Progressive enhancement in the pelvic phase was found in five cases and a slight decreased enhancement in the pelvic phase in two cases. MRI revealed that MA tumor was isointense on T1WI and isointense on T2WI with some slightly hyperintense areas in the center. CTA of the renal arteries revealed the nutrient artery in one patient and no nutrient artery in two. Immunohistochemical experiments demonstrated that most tumor cells were positive for vimentin, CK, and EMA.
Conclusions: MA is a rare benign renal neoplasm. Detailed knowledge of the CT and MRI characteristics of MA plays an important role in MA diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Computer tomography; Magnetic resonance imaging; Metanephric adenoma; Pathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CT imaging spectrum and the histopathological features of adult metanephric adenoma.Br J Radiol. 2015 Jul;88(1051):20140807. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140807. Epub 2015 May 12. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25966289 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging features of metanephric adenoma and their pathological correlation.Clin Radiol. 2019 May;74(5):408.e9-408.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Clin Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30803811
-
[Metanephric Adenoma : A Report of Two Cases].Hinyokika Kiyo. 2018 Aug;64(8):329-333. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_64_8_329. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2018. PMID: 30369221 Japanese.
-
Metanephric Adenoma in the Pediatric Population: Diagnostic Challenges and Follow-up.Urology. 2018 Oct;120:211-215. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2018.06.042. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Urology. 2018. PMID: 30006267 Review.
-
Metanephric adenoma in an 8-year-old child: case report and review of the literature.J Pediatr Surg. 2005 May;40(5):e25-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.02.019. J Pediatr Surg. 2005. PMID: 15937802 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifactor consciousness level assessment of participants with acquired brain injuries employing human-computer interfaces.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Jan 10;19(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12938-019-0746-y. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 31924202 Free PMC article.
-
Experience of diagnosis and management of metanephric adenoma: retrospectively analysis of 10 cases and a literature review.Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Aug;9(4):1661-1669. doi: 10.21037/tau-19-912. Transl Androl Urol. 2020. PMID: 32944527 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

