Angiopoietin-2 impairs collateral artery growth associated with the suppression of the infiltration of macrophages in mouse hindlimb ischaemia
- PMID: 27784306
- PMCID: PMC5080762
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-016-1055-x
Angiopoietin-2 impairs collateral artery growth associated with the suppression of the infiltration of macrophages in mouse hindlimb ischaemia
Abstract
Background: Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), a ligand of the Tie-2 receptor, plays an important role in maintaining endothelial cells and in destabilizing blood vessels. Collateral artery growth (arteriogenesis) is a key adaptive response to arterial occlusion. It is unknown whether the destabilization of blood vessels by Ang-2 can affect arteriogenesis and modulate mononuclear cell function. This study aimed to investigate the effects of Ang-2 on collateral artery growth.
Methods: Hindlimb ischaemia model was produced in C57BL/6 mice by femoral artery ligation. Blood flow perfusion was measured using a laser Doppler perfusion imager quantitative RT-PCR analysis was applied to identify the level of angiogenic factors.
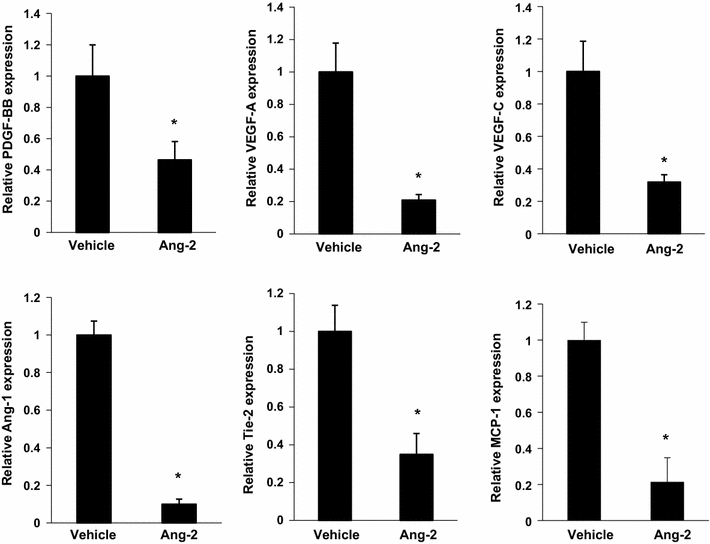
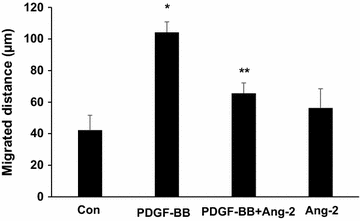
Results: After the induction of hindlimb ischaemia, blood flow recovery was impaired in mice treated with recombinant Ang-2 protein; this was accompanied by a reduction of peri-collateral macrophage infiltration. In addition, quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed that Ang-2 treatment decreased monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) mRNA levels in ischaemic adductor muscles. Ang-2 can lead to macrophage M1/M2 polarization shift inhibition in the ischaemic muscles. Furthermore, Ang-2 reduced the in vitro inflammatory response in macrophages and vascular cells involved in arteriogenesis.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that Ang-2 is essential for efficient arteriogenesis, which controls macrophage infiltration.
Keywords: Angiopoietin-2; Arteriogenesis; Ischaemia; Macrophage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Amplified Arteriogenesis in Collateral Artery Segments Exposed to Reversed Flow Direction.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Nov;35(11):2354-65. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305775. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26338297 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of chemokine (C-x-C motif) ligand 10 diminishes perfusion recovery after local arterial occlusion in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Mar;34(3):594-602. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303050. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24407030
-
P2Y2 nucleotide receptor mediates arteriogenesis in a murine model of hind limb ischemia.J Vasc Surg. 2016 Jan;63(1):216-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.06.112. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Vasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 25088742 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulators of the revascularization response to chronic arterial occlusion.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Mar 15;115(4):701-712. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz001. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 30629133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arteriogenesis: role of nitric oxide.Endothelium. 2003;10(4-5):207-16. doi: 10.1080/10623320390246388. Endothelium. 2003. PMID: 14660080 Review.
Cited by
-
SNRK (Sucrose Nonfermenting 1-Related Kinase) Promotes Angiogenesis In Vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Feb;38(2):373-385. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309834. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29242271 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Prior to Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease Improves Endurance Capacity and Hindlimb Blood Flow by Inhibiting Muscle Inflammation.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 4;8:706491. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.706491. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34422931 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Proangiogenic VEGF-A Is Required for Inflammatory Arteriogenesis During Vascular Injury.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 31;13(4):828. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040828. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299401 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Ang2/Tie2 Axis with Tanshinone IIA Elicits Vascular Normalization in Ischemic Injury and Colon Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Nov 10;2021:7037786. doi: 10.1155/2021/7037786. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34804370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tressel SL, Kim H, Ni CW, Chang K, Velasquez-Castano JC, Taylor WR, Yoon YS, Jo H. Angiopoietin-2 stimulates blood flow recovery after femoral artery occlusion by inducing inflammation and arteriogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:1989–1995. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.175463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

