Belching in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Impedance Study
- PMID: 27784839
- PMCID: PMC5503291
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm16103
Belching in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Impedance Study
Abstract
Background/aims: There are limited data about the relation between belching and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). We aim to evaluate belching in patients with IBS.
Methods: Twenty-five patients with IBS and 12 healthy volunteers were enrolled in the study. IBS was diagnosed in accordance with the Rome III criteria. All patients were questioned about the presence of symptoms for belching, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and dyspepsia. Esophageal manometry and 24-hour pH-impedance were performed in all patients and healthy volunteers. Each of the patients with IBS underwent gastroscopy and colonoscopy.
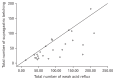
Results: Demographic features were similar in both groups (P > 0.05). The belching rate was 32% in patients with IBS. The mean DeMeester score was significantly higher in IBS patients (13.80 ± 14.40 vs 6.04 ± 5.60, P = 0.027) and 24% of patients had pathologic acid reflux (DeMeester score > 14). Gastroscopy was normal in all patients. Symptom association probability positivity was detected in 24% of patients in the impedance study. The rate of weak acid reflux was also significantly higher in patients with IBS (97.00 ± 56.20 vs 58.20 ± 29.30, P = 0.025). The number of supine gas reflux (7.50 ± 6.40 vs 2.42 ± 2.80, P = 0.001) and supragastric belches was significantly higher in patients with IBS (51.20 ± 41.20 vs 25.08 ± 15.20, P = 0.035). Although the number of gastric belching was higher in controls, the difference did not reach statistical significance (12.10 ± 17.60 vs 4.90 ± 3.80, P = 0.575). We did not find any correlation between belching and any symptoms of IBS.
Conclusions: Belching is frequent in patients with IBS. Non-erosive reflux disease is frequent in IBS, which may be related to supragastric belching.
Keywords: Belching; Gastroesophageal reflux; Impedance; Irritable bowel syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is belching increasing after bariatric bypass surgery in the long term period?Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2021 Oct-Dec;84(4):601-605. doi: 10.51821/84.4.011. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2021. PMID: 34965042
-
Supragastric belching in patients with reflux symptoms.Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Aug;104(8):1992-7. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.203. Epub 2009 May 19. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19455107
-
Postprandial High-Resolution Impedance Manometry Identifies Mechanisms of Nonresponse to Proton Pump Inhibitors.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb;16(2):211-218.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 28911949 Free PMC article.
-
Supragastric belching: Pathogenesis, diagnostic issues and treatment.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2022 May-Jun;28(3):168-174. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_405_21. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35562166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of excessive belching symptoms.Am J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug;109(8):1196-203); (Quiz) 1204. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2014.165. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25001253 Review.
Cited by
-
The Intestinal Gas Questionnaire (IGQ): Psychometric validation of a new instrument for measuring gas-related symptoms and their impact on daily life among general population and irritable bowel syndrome.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022 Mar;34(3):e14202. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14202. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022. PMID: 34145682 Free PMC article.
-
A Predictive Nomogram for the Occurrence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease After Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Study Based on Preoperative HERM.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Nov 4;17:4135-4147. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S484493. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39526204 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

