Comparison of the action of diclofenac alone versus diclofenac plus B vitamins on mobility in patients with low back pain
- PMID: 27785373
- PMCID: PMC5039993
- DOI: 10.3109/21556660.2016.1163263
Comparison of the action of diclofenac alone versus diclofenac plus B vitamins on mobility in patients with low back pain
Abstract
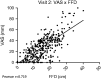
Objective: To assess results of the finger-to-floor distance (FFD) and the Schober test performed during the DOLOR study, and to verify correlation between Visual Analog Pain Scale scores (VAS) with these measures. Research design and methods: Previously tabulated data from the Clinical Research Forms of the DOLOR study were analyzed (statistical significance defined with a two-tailed p value < 0.05 and confidence interval of 95%). For continuous variables, the Student's T- test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used, and differences between pre-treatment and Visits 2, 3, and 4 in the absolute number and percentage of patients with no change, improvement, or worsening of the Schober test and the FFD test scores were calculated, and the results were analyzed with the Chi-squared test. Spearman non-parametric correlation was used for correlating VAS scores with FFD and Schober test scores at each study visit. Main outcome measures: FFD, measured in centimeters; Schober test scores. Results: Throughout the treatment period, there was a statistically significant correlation between the VAS scores and the FFD in the total patient population and within treatment groups. This was not observed for the correlation between the Schober's test scores and the VAS scores. FFD scores within treatment groups improved progressively at each study visit, as did the Schober Test scores. Conclusions: The results of this post-hoc analysis show that combination therapy with diclofenac plus vitamins B1, B6, and B12 had additional positive effects on mobility restoration among the patients of the DOLOR study and serve to highlight the correlation between mobility and pain intensity among patients presenting with low back pain. The two fundamental goals of low back pain therapy are to provide improvements in pain and function. In this sense, the combination of diclofenac with the B vitamins was particularly effective in achieving both of these goals.
Keywords: Low back pain; cyanocobalamin; diclofenac; mobility; pyridoxine; thiamine.
Figures
References
-
- Mibielli MA, Geller M, Cohen JC. Diclofenac plus B vitamins versus diclofenac monotherapy in lumbago: the DOLOR study. CMRO. 2009;25:2589–99. - PubMed
-
- Manek N, MacGregor AJ. Epidemiology of low back disorders. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17:134–40. - PubMed
-
- Breivik H, Callett B, Ventafridda V. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain. 2006;10:287–333. - PubMed
-
- Patrick N, Emanski E, Knaub MA. Acute and chronic low back pain. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:777–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources