Activation of a Habenulo-Raphe Circuit Is Critical for the Behavioral and Neurochemical Consequences of Uncontrollable Stress in the Male Rat
- PMID: 27785462
- PMCID: PMC5066263
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0229-16.2016
Activation of a Habenulo-Raphe Circuit Is Critical for the Behavioral and Neurochemical Consequences of Uncontrollable Stress in the Male Rat
Abstract
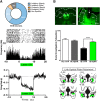
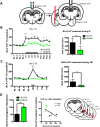
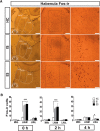
Exposure to uncontrollable stress [inescapable tailshock (IS)] produces behavioral changes that do not occur if the stressor is controllable [escapable tailshock (ES)] an outcome that is mediated by greater IS-induced dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] activation. It has been proposed that this differential activation occurs because the presence of control leads to top-down inhibition of the DRN from medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), not because uncontrollability produces greater excitatory input. Although mPFC inhibitory regulation over DRN 5-HT activation has received considerable attention, the relevant excitatory inputs that drive DRN 5-HT during stress have not. The lateral habenula (LHb) provides a major excitatory input to the DRN, but very little is known about the role of the LHb in regulating DRN-dependent behaviors. Here, optogenetic silencing of the LHb during IS blocked the typical anxiety-like behaviors produced by IS in male rats. Moreover, LHb silencing blocked the increase in extracellular basolateral amygdala 5-HT during IS and, surprisingly, during behavioral testing the following day. We also provide evidence that LHb-DRN pathway activation is not sensitive to the dimension of behavioral control. Overall, these experiments highlight a critical role for LHb in driving DRN activation and 5-HT release into downstream circuits that mediate anxiety-like behavioral outcomes of IS and further support the idea that behavioral control does not modulate excitatory inputs to the DRN.
Keywords: amygdala; habenula; optogenetics; raphe; serotonin; stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dorsal raphe projection inhibits the excitatory inputs on lateral habenula and alleviates depressive behaviors in rats.Brain Struct Funct. 2018 Jun;223(5):2243-2258. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1623-3. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Brain Struct Funct. 2018. PMID: 29460052
-
Effects of GABA microinjection into dorsal raphe nucleus on behavior and activity of lateral habenular neurons in mice.Exp Neurol. 2017 Dec;298(Pt A):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28843542
-
Chemogenetic inhibition of prefrontal cortex inputs to dorsal raphe reduces anxiety behaviors in male rat model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 24;15(1):14397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99181-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40275074 Free PMC article.
-
The role of lateral habenula-dorsal raphe nucleus circuits in higher brain functions and psychiatric illness.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Jan 15;277:89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25234226 Review.
-
The lateral habenula and the serotonergic system.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017 Nov;162:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 17. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2017. PMID: 28528079 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic behavioral studies in depression research: A systematic review.iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109776. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109776. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38726370 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models for the study of depressive disorder.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 Jun;27(6):633-642. doi: 10.1111/cns.13622. Epub 2021 Mar 1. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 33650178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of M-channels in lateral habenula mediates hyperalgesia during alcohol withdrawal in rats.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 25;9(1):2714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38393-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30804373 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation in Effective Treatment and Behavioral Phenotype Between Stress-Enhanced Fear Learning and Learned Helplessness.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 May 15;13:104. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00104. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31156405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol Withdrawal Drives Anxiety-Related Behaviors by Reducing M-type Potassium Channel Activity in the Lateral Habenula.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Aug;42(9):1813-1824. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.68. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28387223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Wang RY (1977) Habenular and other midbrain raphe afferents demonstrated by a modified retrograde tracing technique. Brain Res 122:229–242. - PubMed
-
- Amat J, Matus-Amat P, Watkins LR, Maier SF (1998) Escapable and inescapable stress differentially alter extracellular levels of 5-HT in the basolateral amygdala of the rat. Brain Res 812:113–120. - PubMed
-
- Amat J, Sparks PD, Matus-Amat P, Griggs J, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2001) The role of the habenular complex in the elevation of dorsal raphe nucleus serotonin and the changes in the behavioral responses produced by uncontrollable stress. Brain Res 917:118–126. s - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
