Hes4: A potential prognostic biomarker for newly diagnosed patients with high-grade osteosarcoma
- PMID: 27786411
- PMCID: PMC6240354
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.26318
Hes4: A potential prognostic biomarker for newly diagnosed patients with high-grade osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: Prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma (OS) at the time of diagnosis are lacking. Necrotic response of OS to preoperative chemotherapy correlates with survival and is determined 3-4 months after diagnosis. The purpose of this study is to identify biomarkers that will stratify patients into good or poor responders to chemotherapy at diagnosis and determine the role of potential biomarkers in OS pathogenesis.
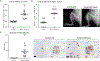
Procedure: Because OS may be caused by disruptions of osteogenic differentiation, and the Notch pathway is one regulator of bone development, we examined the link between Notch effectors, OS differentiation, and OS outcome. We probed the R2: Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform for RNA expression levels of Notch targets in mixed high-grade OS pretreatment biopsies. We used human OS cell lines in vitro and in mice to determine the role of the Notch target hairy/enhancer of split 4 (Hes4) in OS.
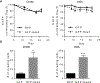
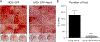
Results: We found that in OS patients, high expression of Hes4 is correlated with decreased metastasis-free and overall survival. Human OS cells that overexpress Hes4 are more immature and have an increased invasive capacity in vitro. This was not universal to all Notch effectors, as Hes1 overexpression induced opposing effects. When injected into NSG mice, Hes4-overexpressing OS cells produced significantly larger, more lytic tumors and significantly more metastases than did control cells.
Conclusions: Hes4 overexpression promotes a more aggressive tumor phenotype by preventing osteoblastic differentiation of OS cells. Hes4 expression may allow for the stratification of patients into good or poor responders to chemotherapy at diagnosis.
Keywords: Hes4; Notch; osteogenic differentiation; osteosarcoma; prognostic factor.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
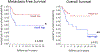

Similar articles
-
Novel basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor hes4 antagonizes the function of twist-1 to regulate lineage commitment of bone marrow stromal/stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Jun 1;24(11):1297-308. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0471. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25579220
-
Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1 promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via matrix metallopeptidase 9 expression.Br J Cancer. 2015 Mar 31;112(7):1232-40. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.84. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25742474 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin-1 enhances experimental osteosarcoma tumor formation and metastasis and is related to poor patient outcome.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jan 17;19(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5303-3. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30654764 Free PMC article.
-
How the NOTCH pathway contributes to the ability of osteosarcoma cells to metastasize.Cancer Treat Res. 2009;152:479-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0284-9_28. Cancer Treat Res. 2009. PMID: 20213410 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in osteosarcoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):20462-20475. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14726. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28103585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HES4 is a potential biomarker for bladder cancer: a Mendelian randomization study.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 21;15(6):1624-1641. doi: 10.7150/jca.92657. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38370367 Free PMC article.
-
A 3D-printed scaffold-based osteosarcoma model allows to investigate tumor phenotypes and pathogenesis in an in vitro bone-mimicking niche.Mater Today Bio. 2022 May 25;15:100295. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100295. eCollection 2022 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 35665234 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of lactate metabolism LncRNAs in the progression and immune microenvironment of osteosarcoma.Transl Oncol. 2023 Oct;36:101753. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101753. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37549606 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Transcriptomic Prognostic Signature by Machine Learning Using a Combination of Small Cohorts of Prostate Cancer.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 25;11:550894. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.550894. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33324443 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic Prostate Cancers with BRCA2 versus ATM Mutations Exhibit Divergent Molecular Features and Clinical Outcomes.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 14;29(14):2702-2713. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3394. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37126020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Winkler K. Osteosarcoma: relationship of response to preoperative chemotherapy and type of surgery to local recurrence. J Clin Oncol. February 1996;14(2):683–684. - PubMed
-
- Bielack SS, Smeland S, Whelan JS, et al. Methotrexate, Doxorubicin, and Cisplatin (MAP) Plus Maintenance Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2b Versus MAP Alone in Patients With Resectable High-Grade Osteosarcoma and Good Histologic Response to Preoperative MAP: First Results of the EURAMOS-1 Good Response Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Oncol. July 10 2015;33(20):2279–2287. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harting MT, Blakely ML, Jaffe N, et al. Long-term survival after aggressive resection of pulmonary metastases among children and adolescents with osteosarcoma. Journal of pediatric surgery. January 2006;41(1):194–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

