Block of both TGF-β and IL-2 signaling impedes Neurophilin-1+ regulatory T cell and follicular regulatory T cell development
- PMID: 27787514
- PMCID: PMC5134002
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.348
Block of both TGF-β and IL-2 signaling impedes Neurophilin-1+ regulatory T cell and follicular regulatory T cell development
Abstract
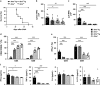
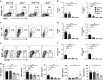
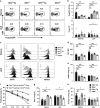
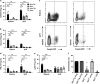
Understanding the mechanisms that lead to autoimmunity is critical for defining potential therapeutic pathways. In this regard there have been considerable efforts in investigating the interacting roles of TGF-β and IL-2 on the function regulatory T cells. We have taken advantage of dnTGF-βRII Il2ra-/- (abbreviated as Il2ra-/-Tg) mouse model, which allows a direct mechanistic approach to define the relative roles of TGF-β and IL-2 on Treg development. Il2ra-/-Tg mice spontaneously developed multi-organ autoimmune diseases with expansion of pathogenic T cells and enhanced germinal center response at 3-4 weeks of age. Importantly, peripheral Treg cells from Il2ra-/-Tg mice demonstrated an activated Th1-like stable phenotype and normal in vitro suppressive function, while thymus Treg increased but manifested decreased suppressive function. Interestingly, neither thymus nor peripheral Treg cells of Il2ra-/-Tg mice contained Neuropilin-1+ or PD-1hi phenotype, resulting in defective follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cell development. Such defective Tfr development led to elevated follicular T helper cells, enhanced germinal center responses and increased plasma cell infiltration. These data demonstrate an important synergetic role of TGF-β and IL-2 in the generation, activation and stability of Treg cells, as well as their subsequent development into Tfr cells.
Figures

References
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003; 299: 1057–1061. - PubMed
-
- Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA et al. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 68–73. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 20–21. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008; 133: 775–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

